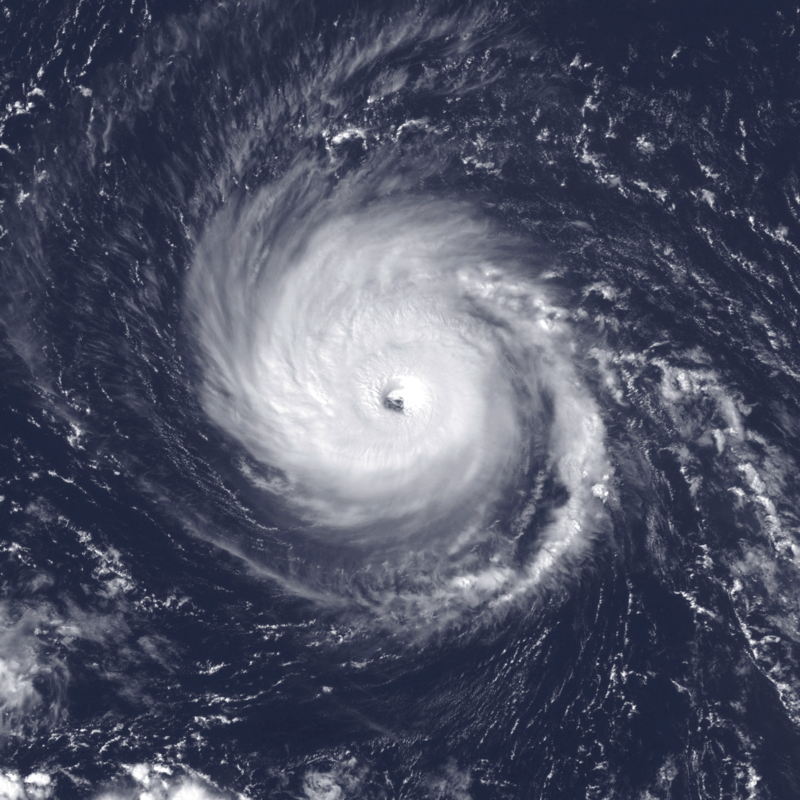
Hurricane Edouard was a notable tropical cyclone that developed during the 2014 Atlantic hurricane season. This research article provides a comprehensive analysis of the storm’s formation, intensification, track, and impacts. Despite remaining at a safe distance from land, Hurricane Edouard generated large swells and dangerous rip currents along the East Coast of the United States. The article also highlights the innovative use of uncrewed drones by NOAA and a NASA-operated Global Hawk in gathering valuable data within the hurricane. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of preparedness and offers recommendations for protecting coastal areas in the event of a similar hurricane threat.
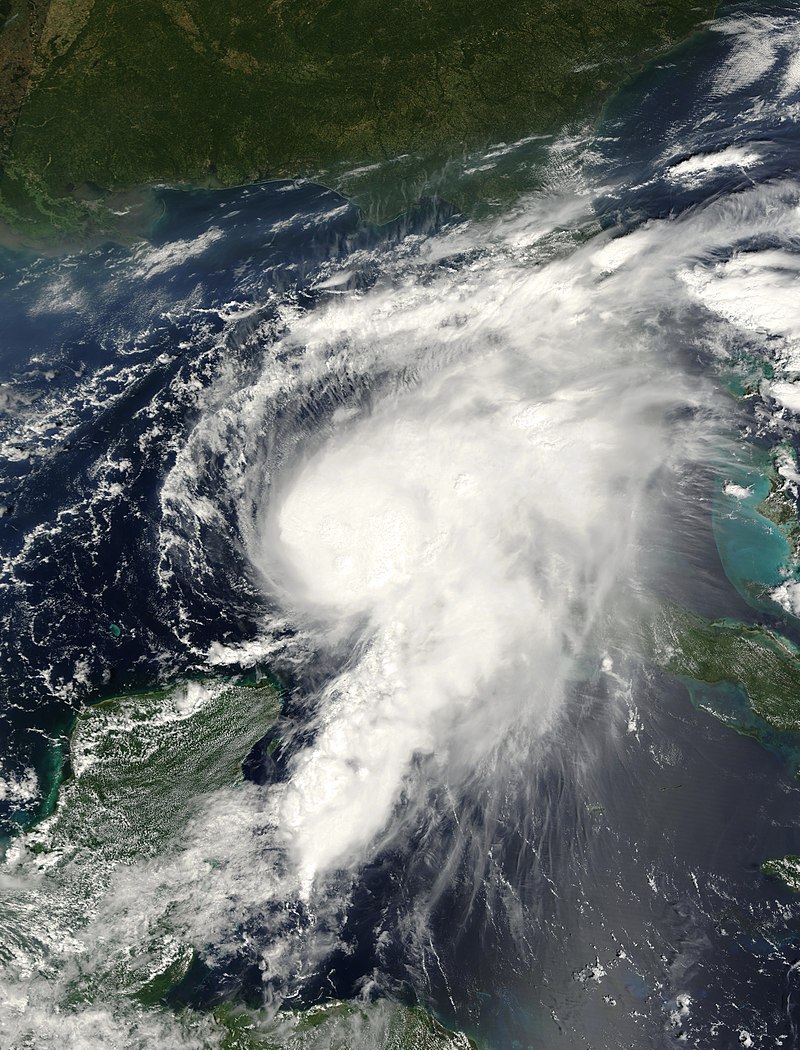
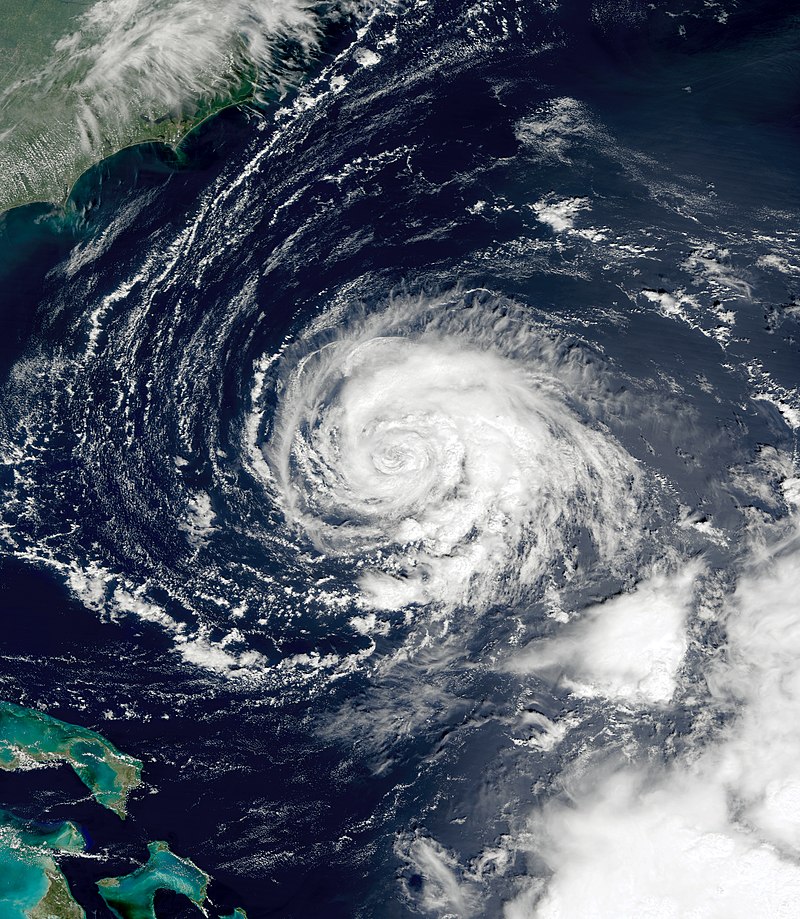
Introduction: Hurricane Edouard originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the western coast of Africa on September 6, 2014. Gradually organizing, it attained tropical depression status by 12:00 UTC on September 11 and strengthened further into Tropical Storm Edouard twelve hours later. The storm’s northwestward trajectory, guided by a subtropical ridge to its northeast, facilitated intensification, leading to hurricane status by 12:00 UTC on September 14. Remarkably, Edouard became a major hurricane with peak winds of 120 mph (195 km/h) at 12:00 UTC on September 16, marking the first major hurricane in the Atlantic since Hurricane Sandy in 2012. Subsequently, the cyclone weakened and degenerated into a remnant low by September 19.
Impacts and Effects: Despite Hurricane Edouard remaining well offshore, its presence had significant repercussions along the East Coast of the United States. The storm generated large swells and dangerous rip currents, leading to multiple fatalities. On September 17, two individuals tragically drowned off the coast of Ocean City, Maryland, due to the strong rip currents associated with Edouard. Rip current warnings were issued for several counties in Florida and Georgia, cautioning residents and visitors about the hazardous conditions.
Coastal Protection and Preparedness: To safeguard lives and property during a potential landfall of a hurricane like Edouard, it is crucial to establish robust preparedness measures. Residents in hurricane-prone areas should remain vigilant and follow the guidance of local authorities. The implementation of the following protective measures is advised:
a) Stay Informed: Regularly monitor weather updates from trusted sources, such as the National Hurricane Center (NHC) and local meteorological agencies. Pay attention to evacuation orders and recommendations issued by local authorities.
b) Emergency Kits and Plans: Prepare emergency supply kits, including non-perishable food, water, medications, batteries, and first aid supplies. Develop a family emergency plan, detailing evacuation routes, communication methods, and designated meeting points.
c) Secure Property: Reinforce homes and buildings against potential storm damage. Trim trees and secure loose objects that could become projectiles in strong winds. Install hurricane shutters or plywood to protect windows and reinforce doors.
d) Evacuation and Sheltering: Follow evacuation orders promptly and seek shelter in designated areas or evacuation centers. Familiarize yourself with the location of these facilities in advance.
Interesting Fact: As a direct result of Hurricane Edouard, the 2014 storm prompted NOAA and NASA to explore innovative technologies for hurricane research. The use of uncrewed drones by NOAA provided crucial lower-level data, enhancing our understanding of the inner workings of hurricanes. Additionally, the deployment of a NASA-operated Global Hawk equipped with advanced instruments expanded our knowledge of temperature, humidity, aerosols, and cloud structure within cyclones. This experience propelled further advancements in hurricane research and contributed to improved forecasting and preparedness efforts.
In conclusion, Hurricane Edouard of the 2014 hurricane season serves as a significant case study for understanding the formation, intensification, and impacts of tropical cyclones. By emphasizing the importance of preparedness and innovative research techniques, this article aims to enhance our ability to mitigate the risks associated with hurricanes similar to Edouard in the future.



Leave a Reply