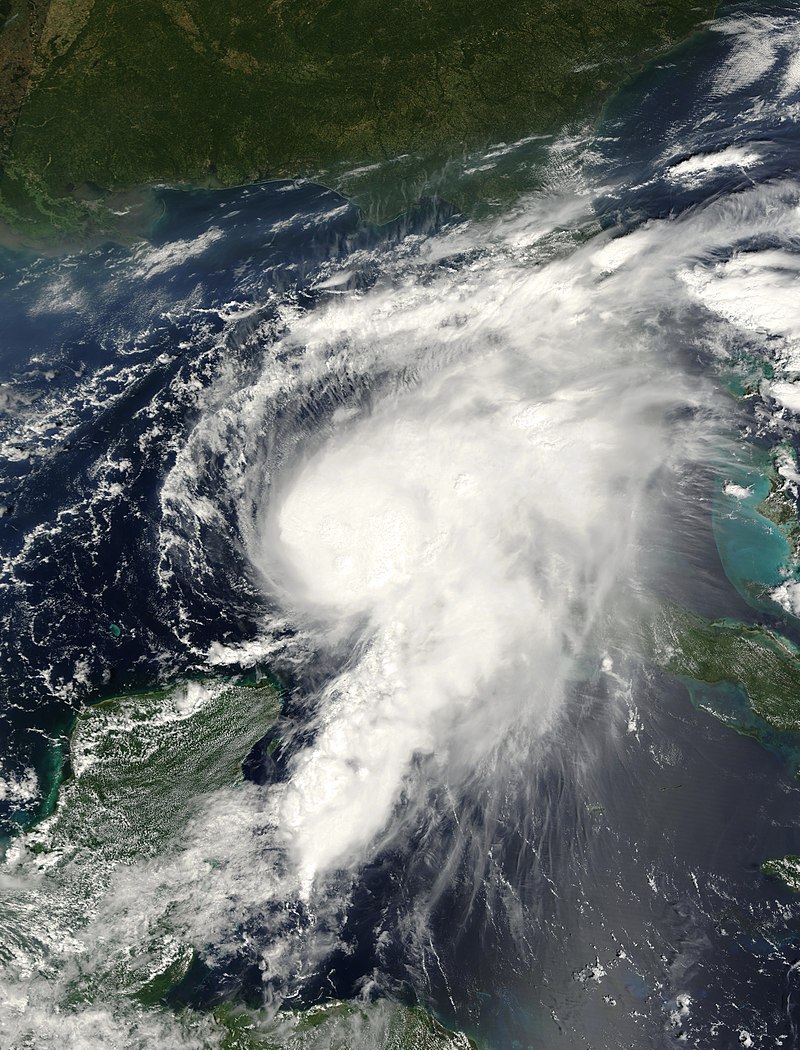
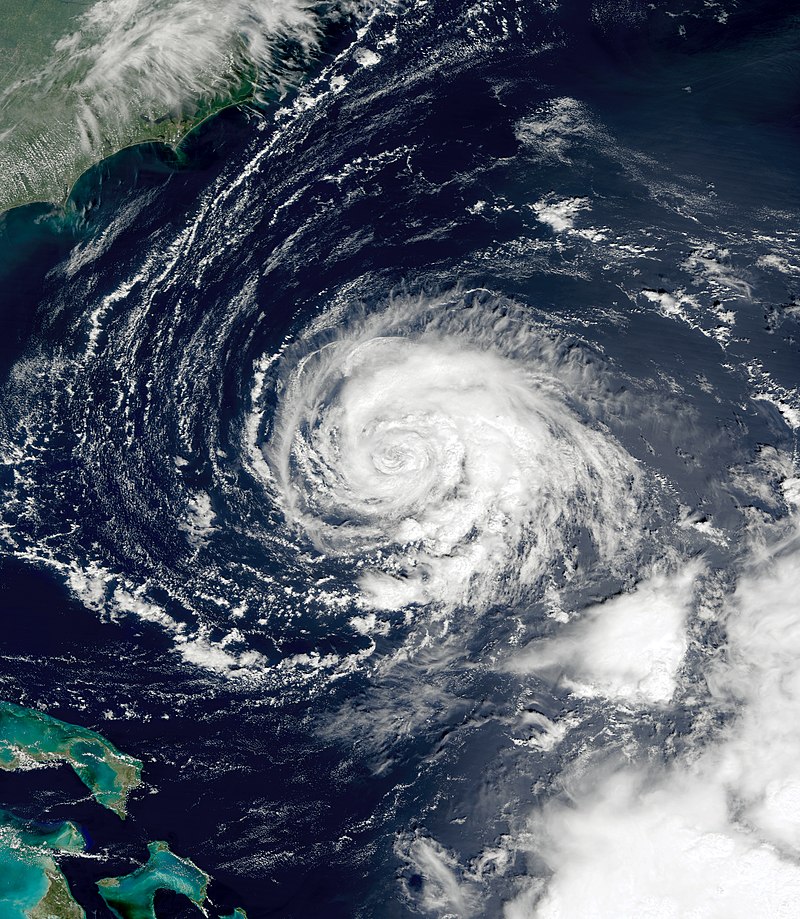
This research article focuses on Hurricane Fabian, a potent Cape Verde hurricane that struck Bermuda in early September during the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season. With a trajectory influenced by the subtropical ridge to its north, Fabian intensified steadily in an environment characterized by warm sea surface temperatures and low wind shear. Attaining a peak intensity of 145 mph (233 km/h) on September 1, the hurricane gradually weakened as it turned northward. On September 5, Fabian made a direct hit on Bermuda with wind speeds exceeding 120 mph (190 km/h). This article examines the impacts of Hurricane Fabian on Bermuda and the surrounding areas, including the damage caused, loss of life, and the subsequent cost of recovery.
Introduction: Hurricane Fabian, the sixth named storm, fourth hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season, originated from a tropical wave in the tropical Atlantic Ocean on August 25. Tracking west-northwestward, Fabian encountered ideal conditions, enabling it to intensify rapidly. As it neared Bermuda, the hurricane grew into the strongest to hit the island since Hurricane Arlene in 1963. Additionally, Fabian became the first hurricane to cause a fatality on Bermuda since 1926.
Impacts on Bermuda: Upon landfall, Hurricane Fabian unleashed its fury on Bermuda, inflicting moderate to severe damage across the island. The powerful winds caused widespread destruction, resulting in roofs being torn off buildings throughout the affected areas. The storm surge associated with Fabian proved particularly hazardous, claiming four lives when individuals were swept away while crossing a causeway, temporarily cutting off the only link between two islands.
The endangered Bermuda petrel, known as the cahow, faced a significant threat due to the hurricane. Ten nests were destroyed, placing the species in jeopardy. Fortunately, dedicated volunteers promptly transported the surviving birds to a safer location, ensuring their preservation.
Impacts Beyond Bermuda: While Bermuda bore the brunt of Fabian’s wrath, other regions also experienced the effects of the hurricane. In northern Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic, strong swells generated by Fabian led to substantial damage. Tragically, four individuals lost their lives along the Atlantic coast of the United States due to rough seas caused by the hurricane.
Damage Assessment and Recovery: The financial toll caused by Hurricane Fabian was significant, with damage estimates totaling around US$300 million. The destruction of infrastructure, along with the loss of property and possessions, added to the overall economic burden. Rebuilding efforts and restoration projects were necessary to recover from the hurricane’s devastating impacts.
Enhancing Preparedness: To mitigate the potential devastation caused by hurricanes similar to Fabian, it is crucial to prioritize preparedness. Residents in hurricane-prone areas should take the following precautions:
Stay informed: Keep track of weather updates and warnings issued by local authorities and meteorological agencies.
Develop an emergency plan: Create a comprehensive plan detailing evacuation routes, designated shelters, and communication methods.
Secure property: Reinforce structures, especially roofs and windows, and trim trees to minimize potential hazards during strong winds.
Assemble an emergency kit: Include essential supplies such as non-perishable food, water, flashlights, batteries, and necessary medications.
Interesting Fact: As a direct result of Hurricane Fabian, the resilience and determination of volunteers and conservationists were highlighted. Through their efforts, the endangered Bermuda petrel, the cahow, was safeguarded from extinction. This serves as a testament to the unwavering dedication of individuals who prioritize the preservation of wildlife even in the face of natural disasters.
Conclusion: Hurricane Fabian, thesixth named storm, fourth hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season, left a lasting impact on Bermuda. With its powerful winds and destructive storm surge, Fabian caused significant damage to infrastructure, destroyed roofs, and resulted in the loss of lives. The hurricane also posed a threat to the endangered Bermuda petrel, but swift action by volunteers ensured the species’ survival.
Beyond Bermuda, Fabian’s effects were felt in northern Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic, where strong swells caused damage, and along the Atlantic coast of the United States, where four individuals tragically drowned. The total cost of the damage caused by Hurricane Fabian amounted to approximately US$300 million, necessitating extensive recovery and rebuilding efforts.
To prepare for future hurricanes like Fabian, it is essential for residents in vulnerable areas to stay informed, develop emergency plans, secure their properties, and assemble emergency kits. By taking these precautions, individuals can enhance their safety and minimize potential damage during severe weather events.
An interesting outcome of the 2003 Hurricane Fabian was the successful rescue and relocation of the endangered Bermuda petrel. The destruction of nests by the hurricane threatened the species, but dedicated volunteers acted swiftly to transport the surviving birds to a safer location. This demonstrates the resilience and commitment of conservationists in protecting endangered wildlife, even in the face of natural disasters.



Leave a Reply