This research article presents a comprehensive analysis of Hurricane Helen, a significant tropical cyclone that developed during the 2018 Atlantic hurricane season. The study investigates the genesis, intensification, track, and impacts of Hurricane Helen from its formation near Africa to its eventual transition into an extratropical cyclone over the British Isles. Additionally, recommendations for preparedness and protection against future hurricanes are provided based on the lessons learned from the impact of Hurricane Helen.
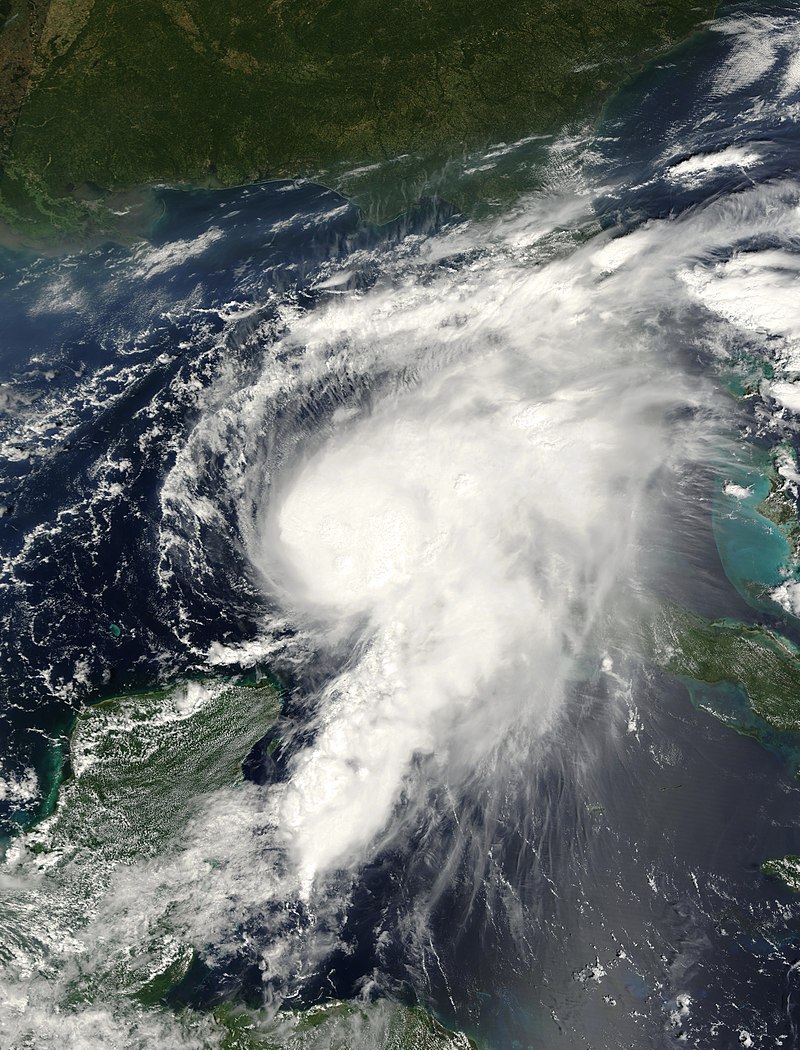
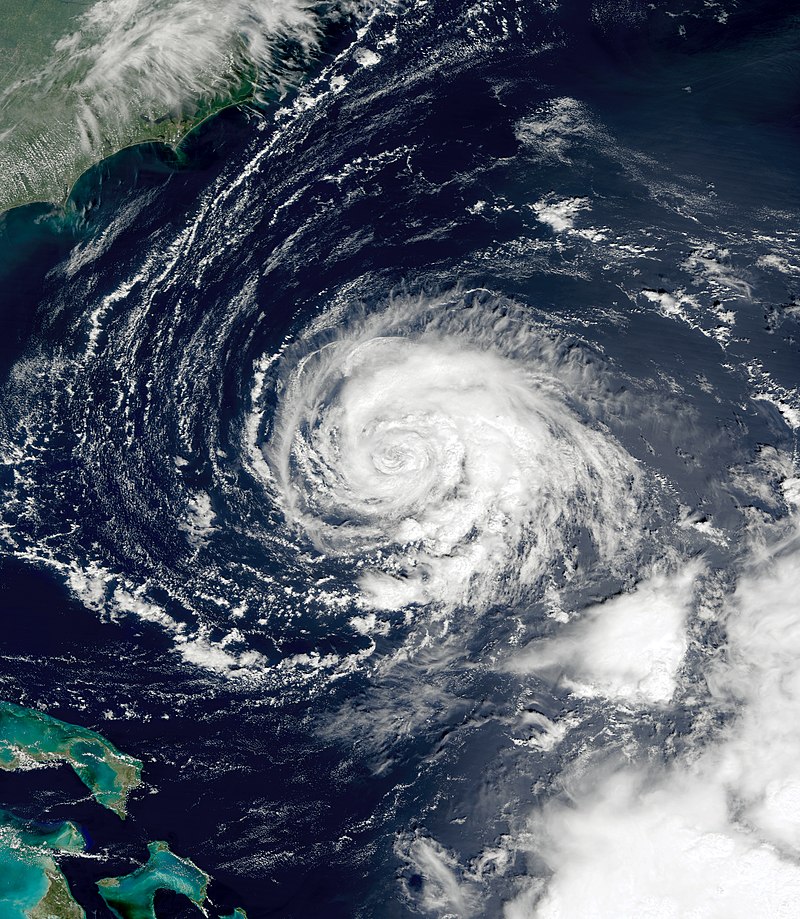
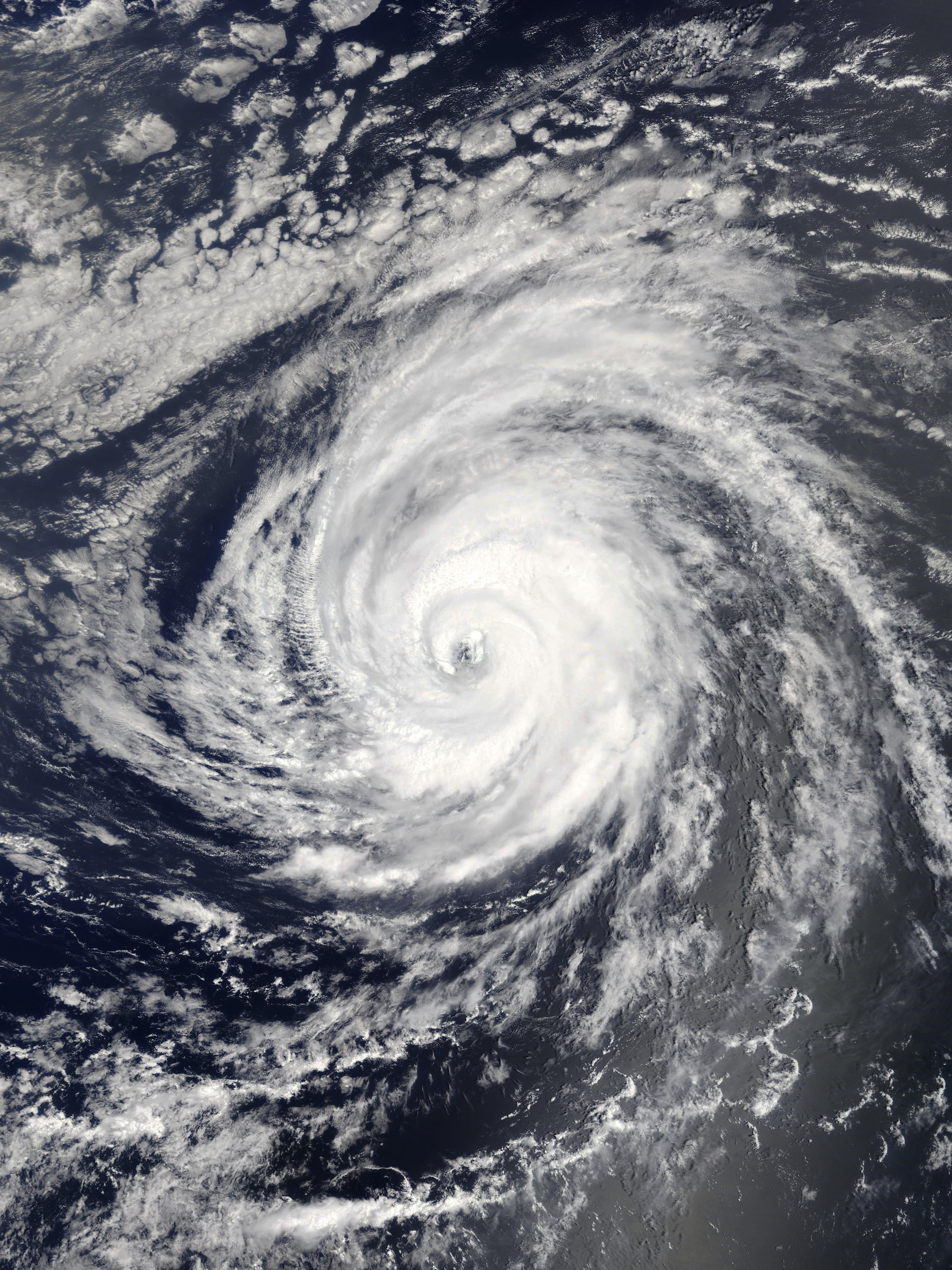
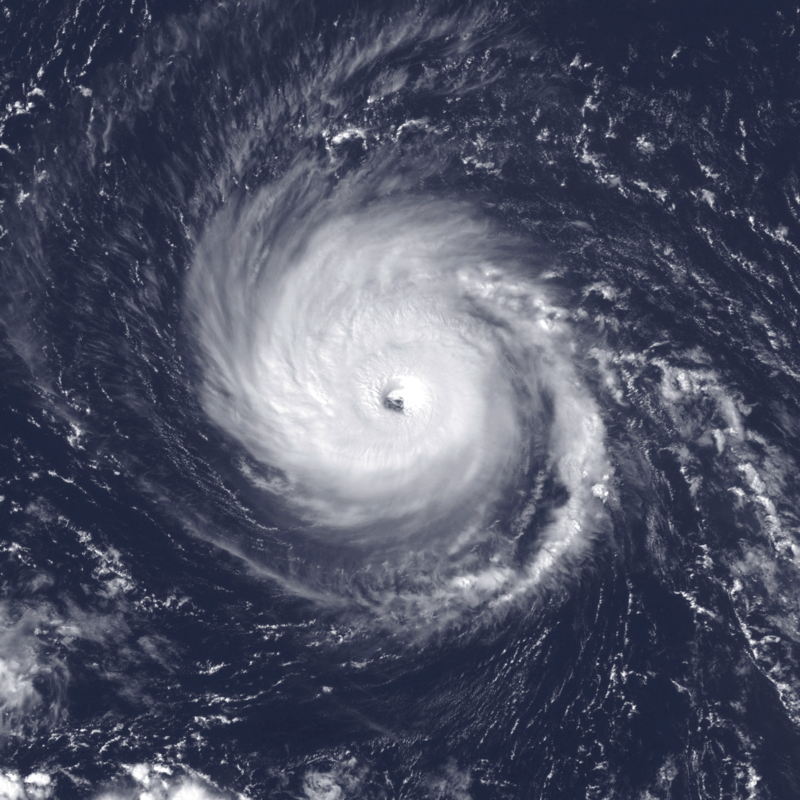
Hurricane Helen: In early September 2018, a vigorous tropical wave traversing west Africa gave rise to a large area of thunderstorm activity, eventually leading to the formation of a tropical depression on September 7 near Banjul, The Gambia. The depression rapidly intensified, reaching hurricane status on September 9 and peaking as a Category 2 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 110 mph (175 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 967 mbar (28.6 inHg) on September 11. The storm, named Hurricane Helen, followed a west-northwestward track before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone over the British Isles.
Impacts: Pre-Landfall: Prior to its landfall, Hurricane Helen affected the Cabo Verde Islands, causing downed trees, damage to infrastructure, and minor destruction to buildings, vehicles, and roads. Fortunately, no casualties were reported in this phase.
Landfall: On September 15, Hurricane Helen made landfall over the Azores, resulting in the likely occurrence of tropical storm-force winds across the western Azores. Damage assessments and reports of casualties in this region are limited, highlighting the need for further investigation into the storm’s impact on these islands.
Post-Landfall: After transitioning into an extratropical cyclone, the remnants of Hurricane Helen impacted Ireland and the United Kingdom. While the storm weakened considerably, it still caused rainfall across the British Isles and recorded wind gusts of up to 50 mph (80 km/h) in Wales. Fortunately, there were no reported fatalities associated with the storm’s passage over these regions.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations: Based on the impact of Hurricane Helen, it is crucial for individuals and communities residing in hurricane-prone areas to take necessary precautions to mitigate risks and enhance preparedness. The following recommendations are provided for future hurricane events:
Early Warning Systems: Investments in early warning systems, such as improved meteorological monitoring and accurate forecasting, are essential to provide timely and precise information to vulnerable communities. Increased public awareness and education regarding hurricane preparedness should also be prioritized.
Evacuation Plans: Local authorities must develop and communicate effective evacuation plans, particularly for areas prone to storm surge and flooding. Clear instructions and designated evacuation routes are crucial for ensuring the safety of residents.
Infrastructure Resilience: Strengthening infrastructure to withstand hurricane impacts, including reinforced buildings, flood mitigation measures, and improved coastal protection, can significantly minimize damage and aid in post-hurricane recovery efforts.
Interesting Fact: As a direct result of Hurricane Helen, the storm’s transition into an extratropical cyclone over the British Isles marked the beginning of the European windstorm season. This event highlighted the interconnectedness of weather systems across different regions and emphasized the need for comprehensive international collaboration in tracking and forecasting extreme weather events.
In conclusion, Hurricane Helen’s journey from its genesis near Africa to its impact on the Azores, Ireland, and the United Kingdom in 2018 serves as a valuable case study for understanding the dynamics of tropical cyclones and the subsequent challenges faced by affected regions. By learning from the experiences of past hurricanes


Leave a Reply