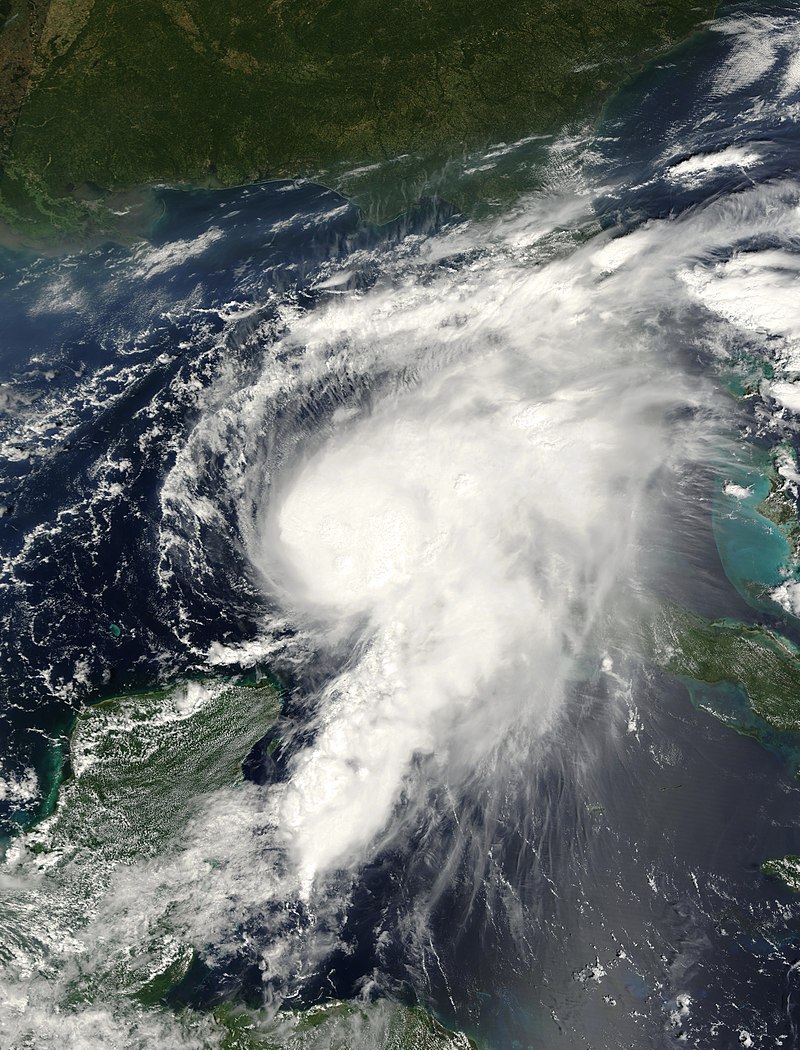
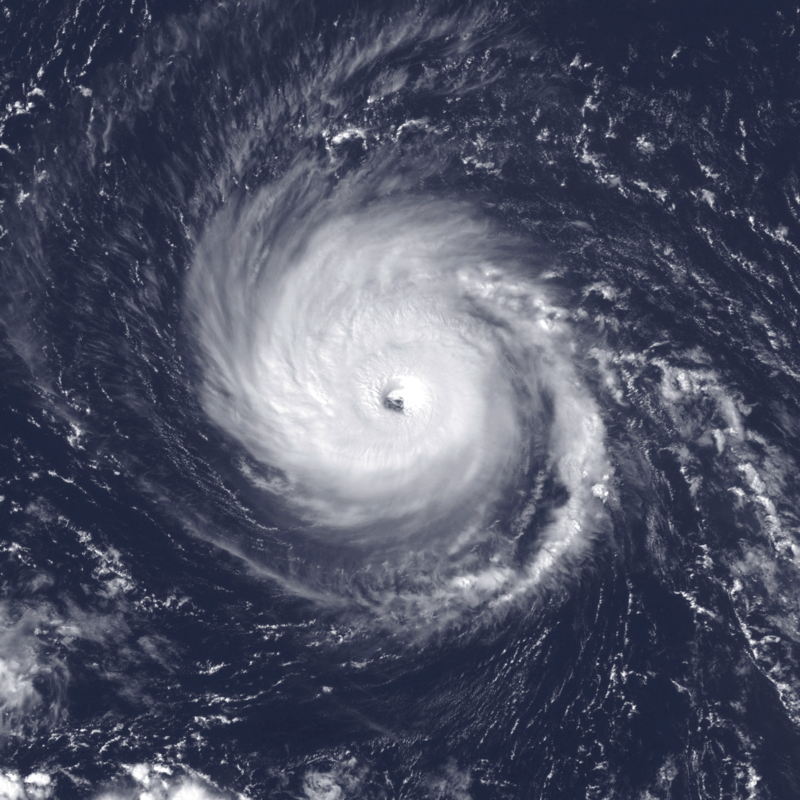
This research article presents a comprehensive analysis of Hurricane Karen, which emerged as a large tropical wave accompanied by a broad low-pressure system off the coast of Africa on September 21 during the 2007 hurricane season. As it traversed westward, the disturbance gradually intensified, leading to the formation of a tropical depression on September 24. Within six hours, it further strengthened and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Karen. However, Karen’s path was riddled with challenges, as it encountered unfavorable atmospheric conditions and underwent fluctuations in intensity. Eventually, the storm dissipated in the mid-Atlantic on September 29, leaving its remnants near the Leeward Islands. Fortunately, Karen did not directly impact any land areas, resulting in no reported damages or casualties.
Introduction: During the 2007 hurricane season, Hurricane Karen stood as a noteworthy tropical cyclone due to its origins as a substantial tropical wave with a well-defined low-pressure envelope off the African coast. This article aims to explore the genesis, intensification, dissipation, and the absence of significant impacts associated with Hurricane Karen.
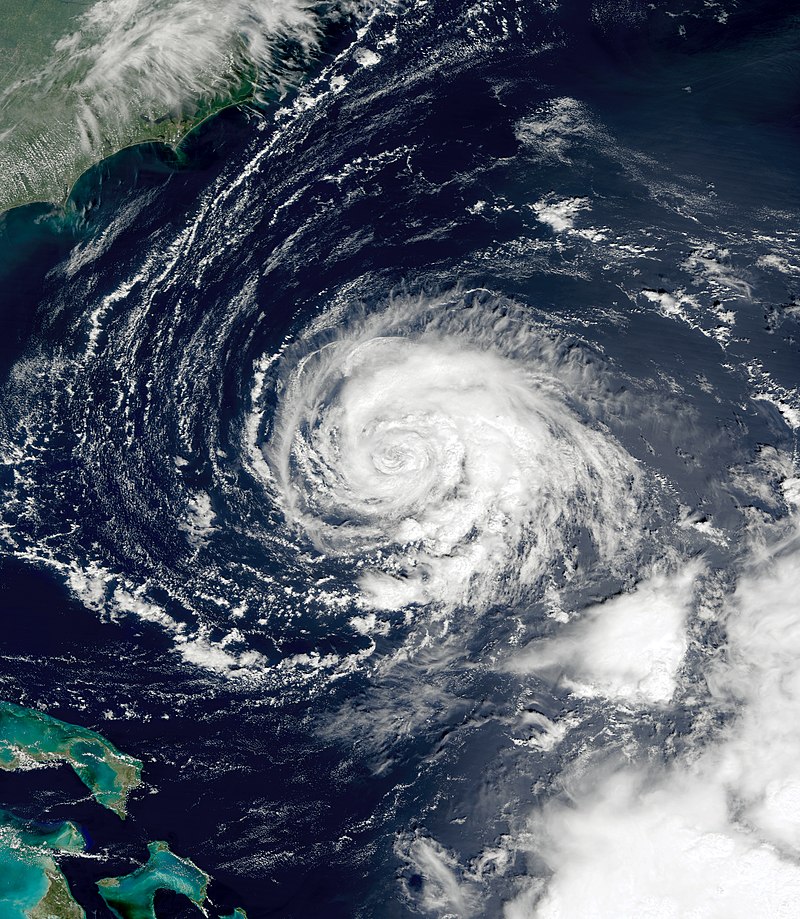
Genesis and Intensification: Emerging from Africa on September 21, the tropical wave steadily gained organization as deep convection increased and its low-level circulation became more pronounced. By September 24, it developed into a tropical depression, and within hours, the system intensified further, earning the designation of Tropical Storm Karen. Throughout September 25, Karen maintained its intensity, and early on September 26, it experienced significant strengthening, reaching hurricane status for approximately twelve hours. However, this growth was short-lived, as a powerful upper-level trough induced increased vertical wind shear, weakening Karen’s structure and exposing its large low-level circulation.
Impact and Dissipation: By September 28, the unfavorable atmospheric conditions had diminished Karen’s strength to a marginal tropical storm, with its circulation exposed. The storm altered its trajectory, heading northward, and intermittently experienced bursts of deep convection. Nevertheless, the relentless wind shear ultimately led to Karen’s dissipation in the mid-Atlantic on September 29. Notably, the remnants of Karen lingered near the Leeward Islands for a few days without directly impacting any land areas.
Lessons Learned and Preparedness: While Hurricane Karen did not cause significant damage or result in any reported casualties, its path serves as a reminder of the potential threats posed by tropical cyclones. To ensure preparedness for future hurricanes, it is crucial for individuals residing in hurricane-prone regions to follow these guidelines:
- Stay informed: Regularly monitor weather forecasts and official advisories issued by local authorities to stay updated on the development and trajectory of approaching storms.
- Develop an emergency plan: Create a comprehensive plan that includes evacuation routes, designated meeting points, and arrangements for pets, vulnerable individuals, and essential documents.
- Assemble an emergency kit: Stock up on essential supplies, such as non-perishable food items, water, batteries, flashlights, first aid supplies, and important medications.
- Secure your property: Prior to hurricane threats, reinforce windows, doors, and roofs, trim trees and shrubs, and secure loose outdoor items that could become hazardous during strong winds.
- Evacuate when necessary: Follow evacuation orders issued by local authorities to ensure personal safety. Plan in advance for alternative accommodation options if evacuation becomes mandatory.
- Communication and community support: Establish communication networks with family, friends, and neighbors to stay connected during emergencies. Support one another and consider vulnerable individuals within the community who may need assistance.
Interesting Fact: As a direct result of Hurricane Karen in 2007, meteorologists and researchers intensified efforts to improve hurricane forecasting models, enhancing the accuracy of track predictions and intensity forecasts. This ongoing development in hurricane science has significantly contributed to better preparedness, allowing communities to make informed decisions and potentially reduce the risks associated with tropical cyclones.
Conclusion: Through a comprehensive analysis of Hurricane Karen from the 2007 hurricane season, this research article highlights the storm’s genesis, intensification, dissipation, and the absence of significant impacts. While Karen did not directly affect land areas, it serves as a reminder of the importance of preparedness in hurricane-prone regions. By following proper safety protocols and staying informed, individuals and communities can mitigate potential risks and protect lives and property when faced with the threat of a hurricane.



Leave a Reply