This research article examines the significant meteorological and societal impacts of Hurricane Nate 2017 during the exceptionally active 2017 Atlantic hurricane season. Originating from a broad area of low pressure in the southwestern Caribbean, Hurricane Nate rapidly intensified and caused severe flooding, destruction, and casualties in Central America before making landfall along the US Gulf Coast. The hurricane set several records, including being the fastest-moving tropical system ever recorded in the Gulf of Mexico. Furthermore, its landfall in Costa Rica marked the costliest natural disaster in the country’s history. This article provides detailed insights into the areas affected by Hurricane Nate before, during, and after landfall, highlighting the damage incurred, loss of life, and subsequent rebuilding efforts. Additionally, recommendations for enhancing preparedness and protection against future hurricanes similar to Nate are discussed.
Introduction: Hurricane Nate, the fourteenth named storm and ninth hurricane of the highly active 2017 Atlantic hurricane season, developed from a disturbance in the southwestern Caribbean on October 3. It intensified quickly, bringing devastating impacts to Central America before reaching the US Gulf Coast. This article aims to analyze the destructive forces unleashed by Hurricane Nate and shed light on the lessons learned from this event to better prepare for future storms.
Impact on Central America: Hurricane Nate 2017 caused extensive flooding and widespread destruction in Central America, leading to significant loss of life and infrastructure damage. Nicaragua and Costa Rica were severely affected, with Nicaragua recording 16 fatalities and Costa Rica suffering 14 deaths, making it the costliest natural disaster in the nation’s history. Additionally, Guatemala, Panama, Honduras, and El Salvador reported a combined total of 16 casualties. The storm’s heavy rainfall triggered landslides and caused rivers to overflow, leading to the displacement of thousands of people and the destruction of homes and vital infrastructure.
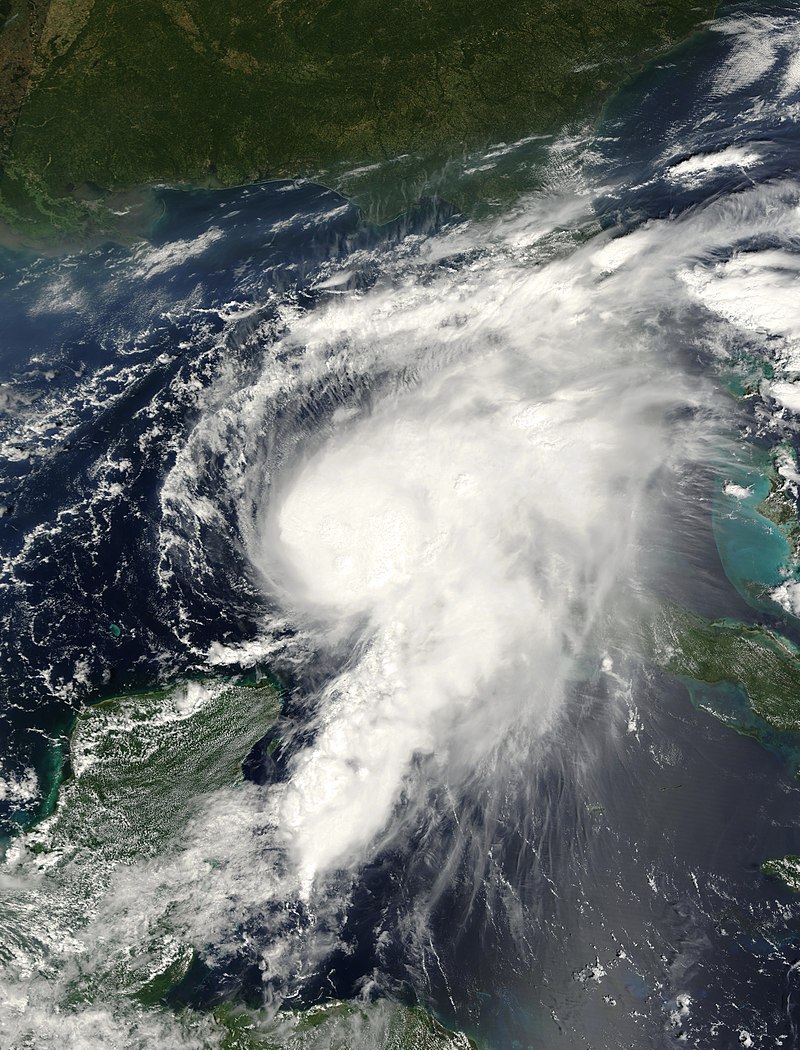
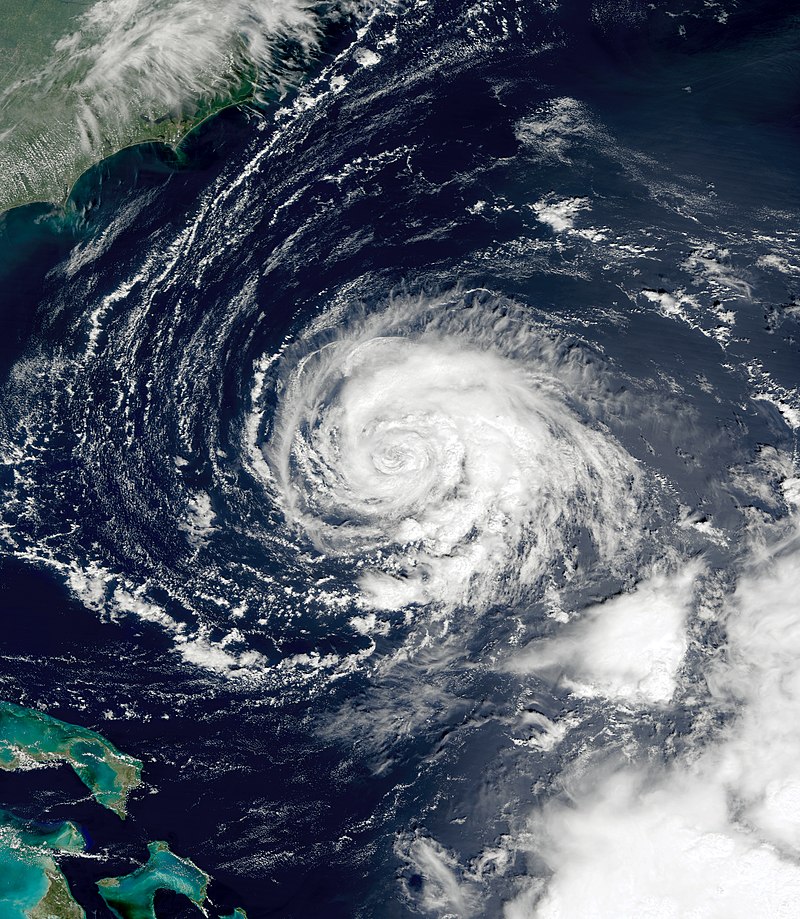
Landfall on the US Gulf Coast: After devastating Central America, Hurricane Nate continued to intensify over the warm waters of the northwestern Caribbean Sea. It reached hurricane strength while traversing the Yucatán Channel, with peak winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) recorded in the central Gulf of Mexico on October 7. Early on October 8, Nate made landfall near the mouth of the Mississippi River in Louisiana. It then struck Biloxi, Mississippi, causing storm surges, rip currents, hurricane-force winds, and beach erosion. Notably, Nate marked the first tropical cyclone to make landfall in Mississippi since Hurricane Katrina in 2005.
Impact on Affected Areas and Rebuilding Efforts: Hurricane Nate’s fast movement compounded its destructive potential. The storm surge flooded the ground floors of coastal casinos and buildings, resulting in significant damage to infrastructure and property. Additionally, widespread power outages and disruptions to transportation networks were observed. In terms of human casualties, the United States reported two deaths, emphasizing the importance of timely evacuation and adherence to safety protocols during hurricane events. The cost of cleaning and rebuilding in the affected areas, both in Central America and the US Gulf Coast, reached significant figures, highlighting the magnitude of the destruction caused by Hurricane Nate 2017.
Enhancing Preparedness and Protection: To ensure better preparedness for future hurricanes, it is crucial for communities and individuals to be aware of their vulnerability and take appropriate precautions. Some measures that can be undertaken include developing robust evacuation plans, reinforcing infrastructure, promoting public awareness campaigns, and establishing early warning systems. Improved forecasting capabilities and communication networks are also essential for disseminating accurate and timely information to residents in at-risk regions.
Interesting Fact: As a direct result of Hurricane Nate, the United States Coast Guard reported a significant rise in the number of beached and stranded marine animals, including dolphins and sea turtles, along the Gulf Coast. This phenomenon was attributed to the storm’s powerful winds and the disturbance it caused in the marine ecosystem. Efforts were made to rescue and rehabilitate these stranded animals, emphasizing the interconnectedness between severe weather events and the environment.
In conclusion, Hurricane Nate’s devastating impact on Central America and the US Gulf Coast during the 2017 hurricane season serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of tropical cyclones. Learning from this event, communities must continue to improve their preparedness and response strategies to mitigate the potential damage caused by future hurricanes.



Leave a Reply