Hurricane Cindy, a tropical cyclone that briefly attained minimal hurricane strength, left its mark on the Gulf of Mexico during the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season. Initially categorized as a tropical storm, post-season analysis upgraded Cindy to a Category 1 hurricane. This research article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Hurricane Cindy, including its formation, landfall in Louisiana, and subsequent impacts. The storm, which caused heavy rains, flooding, fatalities, and property damage, serves as a reminder of the importance of preparedness and mitigation strategies in hurricane-prone areas.
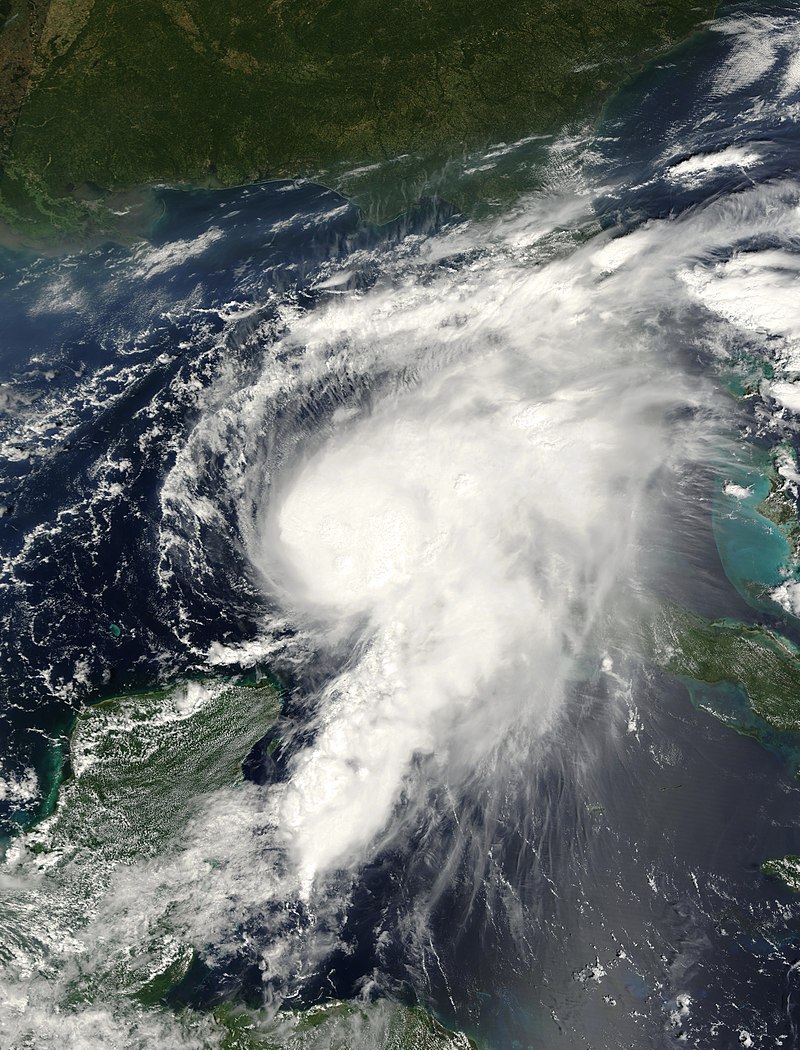
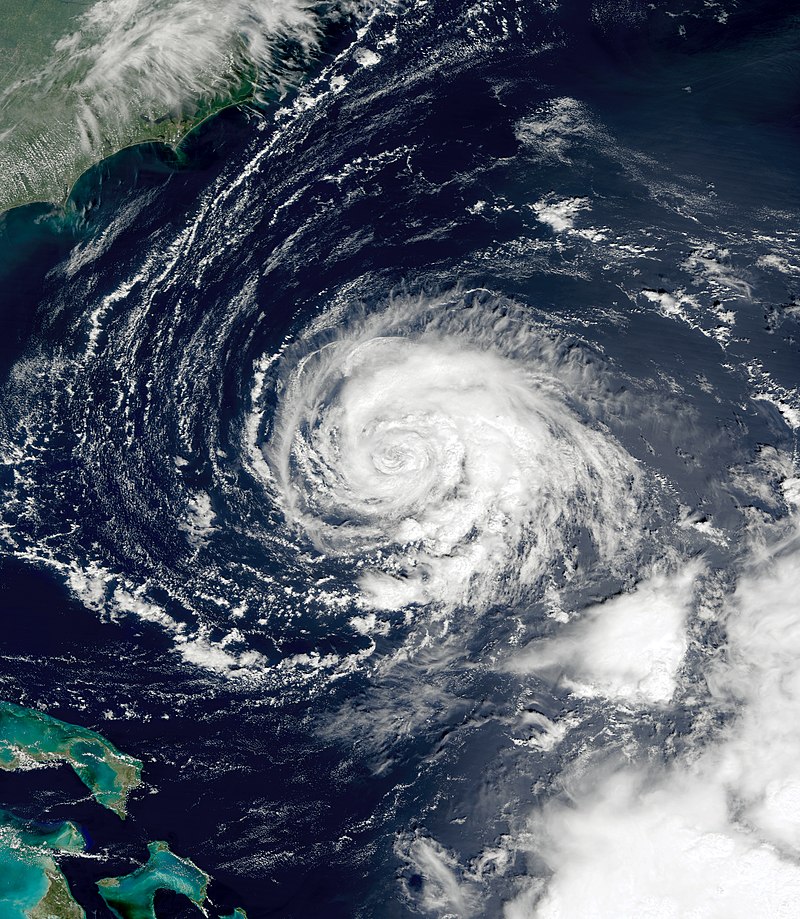
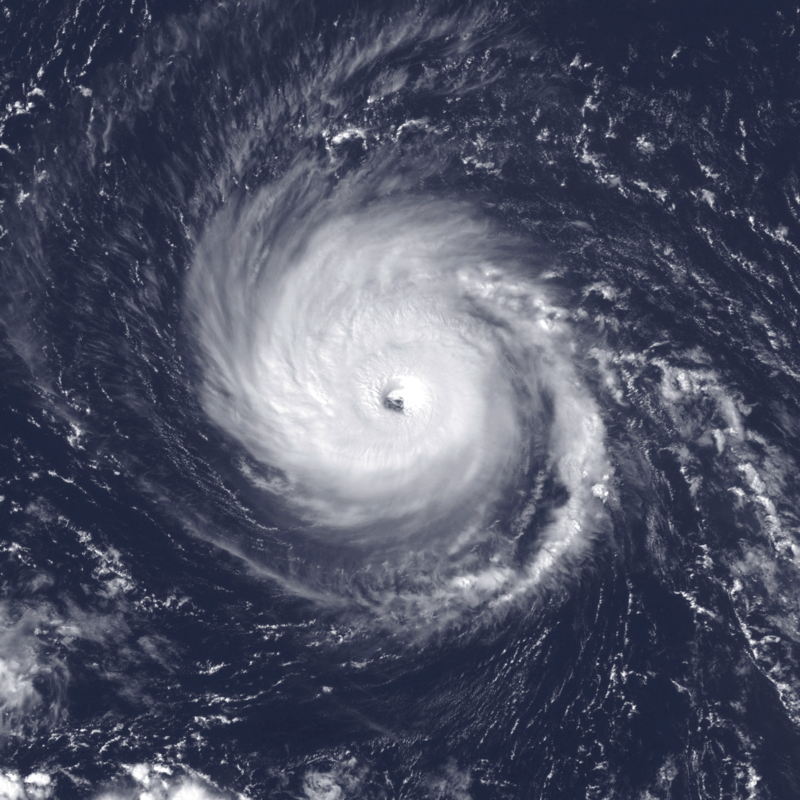
Introduction: Hurricane Cindy, the third named storm and first hurricane of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season, emerged as a tropical depression on July 3, east of the Yucatán Peninsula in the Caribbean Sea. After making landfall on the peninsula, the storm weakened before reentering the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico on July 4. Gradually intensifying, Cindy reached hurricane strength just before striking near Grand Isle, Louisiana, on July 5. The storm’s landfall was followed by a gradual weakening trend, and it transitioned into an extratropical system on July 7.
Impacts: Before Landfall: As Hurricane Cindy approached the Gulf Coast, coastal regions were placed under hurricane warnings, triggering precautionary measures and evacuations. Residents in Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and neighboring areas were advised to monitor the storm’s progress and make necessary preparations.
During Landfall: When Hurricane Cindy made landfall near Grand Isle, Louisiana, it brought strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge to the affected areas. The storm caused significant property damage, primarily due to wind and flooding. Coastal regions experienced erosion, while low-lying areas were inundated by storm surge and excessive rainfall. Local infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and power lines, suffered substantial damage.
Loss of Life: Hurricane Cindy resulted in three deaths in the United States. These tragic losses underscore the need for heightened awareness and preparedness when facing severe weather events.
After the Hurricane: In the storm’s aftermath, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Maryland were left grappling with the aftermath of flooding and damage. The affected regions faced the arduous task of cleaning up debris, restoring power, and repairing damaged structures. The economic impact of Hurricane Cindy’s destruction included costs associated with infrastructure repairs, property restoration, and the disruption of economic activities. Accurate estimations of these costs are essential for future planning and preparedness.
Protective Measures: To minimize the risks associated with hurricanes like Cindy, it is crucial to adopt appropriate protective measures. This includes:
- Stay informed: Remain updated with the latest weather forecasts, watches, and warnings issued by meteorological authorities.
- Emergency preparedness: Develop a hurricane preparedness plan, including evacuation strategies, emergency supplies, and communication protocols.
- Secure property: Take measures to reinforce homes and buildings, such as installing hurricane shutters, reinforcing doors and windows, and securing loose objects outdoors.
- Evacuation readiness: Familiarize yourself with evacuation routes and heed evacuation orders from local authorities promptly.
- Insurance coverage: Ensure that your property and belongings are adequately insured against potential hurricane damage.
Interesting Fact: In the wake of Hurricane Cindy, communities in affected regions collaborated on the development and implementation of improved emergency response and disaster management strategies. This event highlighted the resilience and adaptability of communities when faced with the challenges posed by tropical cyclones.
Conclusion: Hurricane Cindy, despite its brief stint as a hurricane, left a lasting impact on the Gulf of Mexico and adjacent regions during the 2005 hurricane season. The storm’s heavy rains, flooding, property damage, and unfortunate loss of life underscore the necessity of preparedness and resilience in hurricane-prone areas. By adopting protective measures, staying informed, and working together, communities can better mitigate the effects of future hurricanes and build a more resilient future.



Leave a Reply