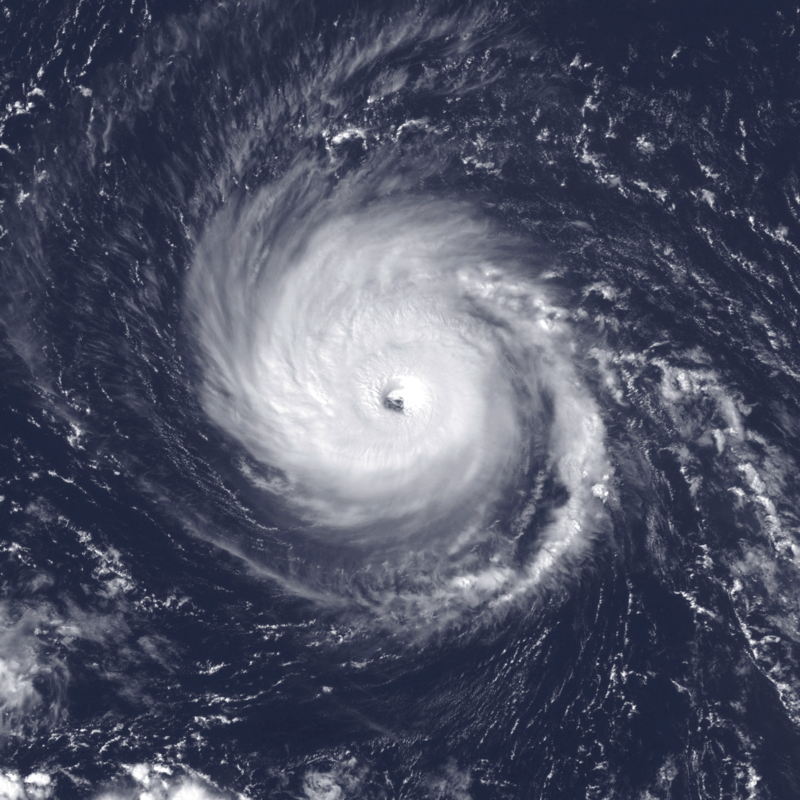
Hurricane Felix, a powerful Category 5 Atlantic hurricane, made landfall on September 4, 2007, just south of the Nicaragua-Honduras border. This research article provides an in-depth analysis of the storm’s characteristics, impacts, and historical significance. Felix set a new record as the southernmost-landfalling Category 5 storm, surpassing Hurricane Edith of 1971. The storm caused significant devastation, resulting in numerous fatalities, extensive damage, and substantial economic costs. This article also provides valuable insights on preparedness measures for future hurricanes similar to Felix.
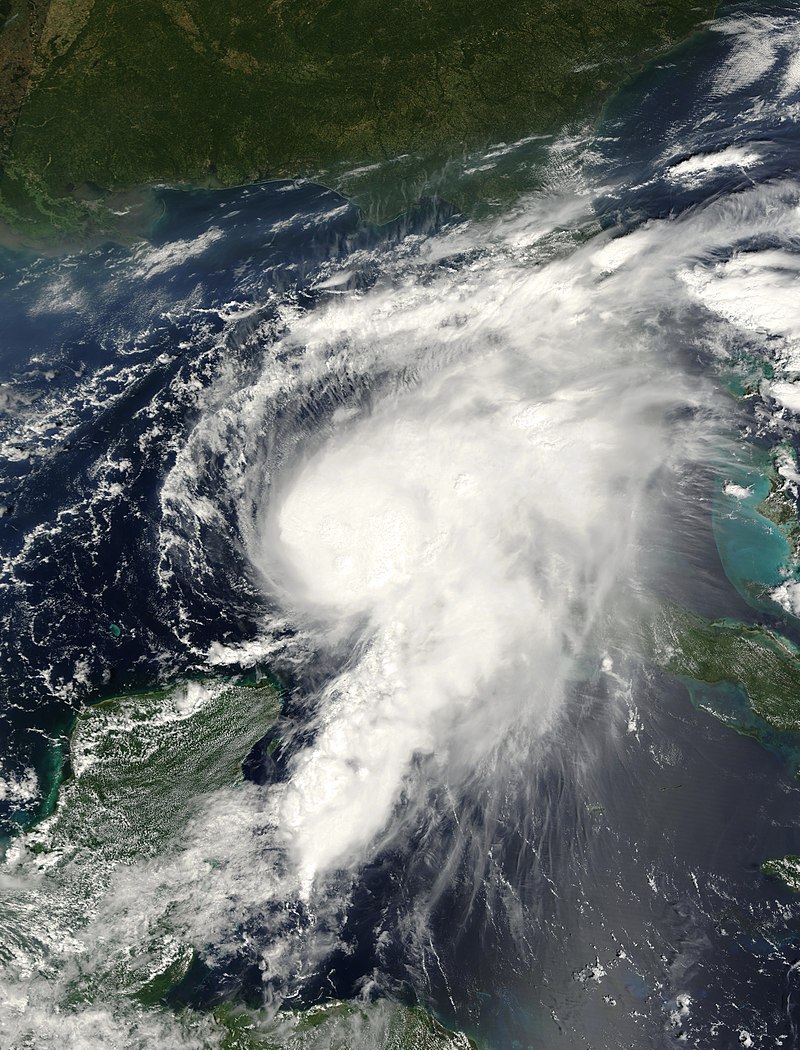
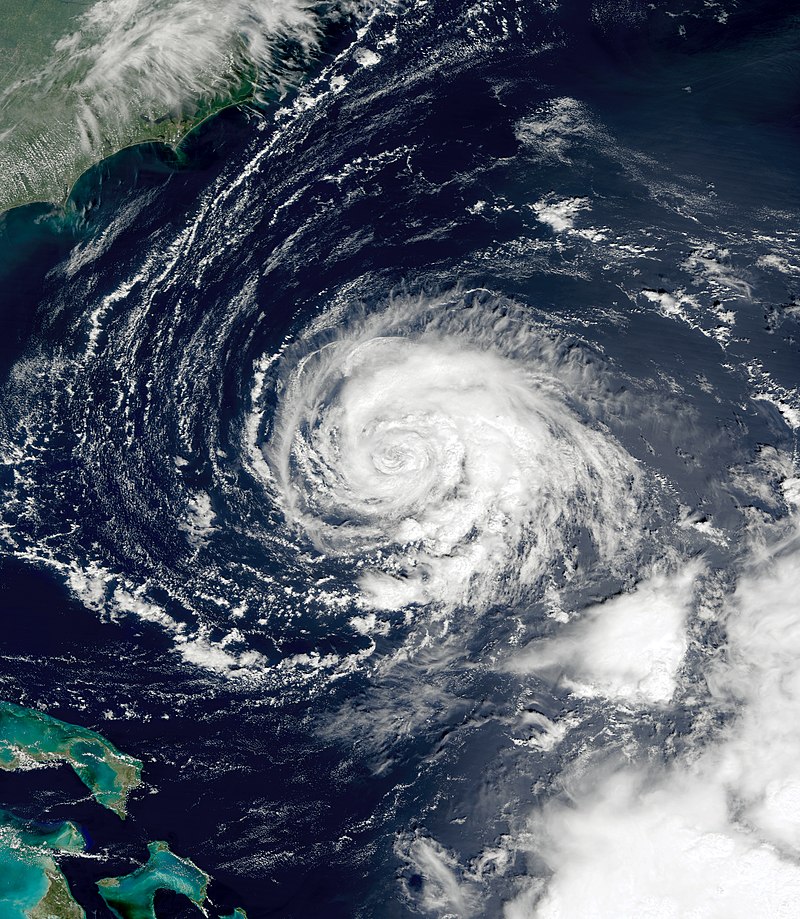
Introduction: Hurricane Felix formed from a tropical wave on August 31, 2007, and intensified rapidly after passing through the southern Windward Islands on September 1. By September 3, it reached Category 5 status, only to be downgraded to Category 4 later that day. However, it regained Category 5 strength by the morning of September 4, just prior to making landfall in Central America.
Impacts Before Landfall: Before reaching Central America, Hurricane Felix had already exhibited its destructive potential. The storm’s outer bands brought heavy rainfall and strong winds to several Caribbean islands, including Grenada, Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao. Although these areas did not experience direct landfall, they faced localized flooding, property damage, and disrupted infrastructure.
Landfall and Devastation: On September 4, Felix made landfall in northeastern Nicaragua, near the Nicaragua-Honduras border. The storm unleashed its full fury, resulting in extensive destruction and loss of life. The immediate coastal regions, including Puerto Cabezas and surrounding areas, bore the brunt of the storm’s devastating winds, torrential rainfall, and storm surge. The hurricane’s impact extended into eastern Honduras as well.
Loss of Life and Damage: Tragically, Hurricane Felix caused at least 133 deaths, primarily in Nicaragua and Honduras. The storm’s powerful winds, intense rainfall, and subsequent flooding led to significant destruction of homes, infrastructure, and agriculture. The combined effects resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars in damages, with Nicaragua suffering the most severe consequences.
Post-Landfall Recovery and Rebuilding: In the aftermath of Hurricane Felix, affected areas faced immense challenges in terms of recovery and rebuilding. Emergency response efforts focused on providing immediate relief, including search and rescue operations, medical assistance, and the distribution of essential supplies. Governments, international organizations, and humanitarian agencies coordinated their efforts to restore infrastructure, support displaced communities, and address the long-term needs of affected populations.
Preparedness Measures for Future Hurricanes: To mitigate the impact of future hurricanes like Felix, it is crucial to prioritize preparedness. Communities in hurricane-prone areas should have well-defined evacuation plans, early warning systems, and robust communication channels to disseminate critical information. Adequate infrastructure, including storm shelters, flood protection measures, and reinforced buildings, can significantly reduce the vulnerability of coastal regions.
Interesting Fact: As a direct result of Hurricane Felix, the name “Felix” was retired from the rotating list of hurricane names for the Atlantic Basin. This decision was made by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) due to the storm’s devastating impact on Central America in 2007. The naming of hurricanes allows for easier identification and tracking, and the retirement of a name symbolizes the severity and lasting impact of the storm.
In conclusion, Hurricane Felix, the southernmost-landfalling Category 5 storm on record, left a lasting impact on Central America in 2007. The storm’s destructive forces caused numerous casualties, extensive damage, and economic losses. By learning from the lessons of Felix, communities can better prepare for future hurricanes and minimize their impact, ultimately safeguarding lives and property in vulnerable regions.



Leave a Reply