Hurricane Ingrid, which formed during the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, had significant implications for the eastern coast of Mexico. This research article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Hurricane Ingrid, including its formation, track, and impact on the affected regions. The storm emerged from a tropical wave that developed into a tropical depression in the Bay of Campeche, eventually intensifying into a hurricane. Ingrid struck northeastern Mexico, coinciding with the aftermath of Hurricane Manuel on the Pacific coast. The combined effects of both storms resulted in widespread destruction, loss of life, and significant economic consequences. This article presents an analysis of the areas impacted, the damage incurred, and measures that can be taken to enhance preparedness for future hurricanes.
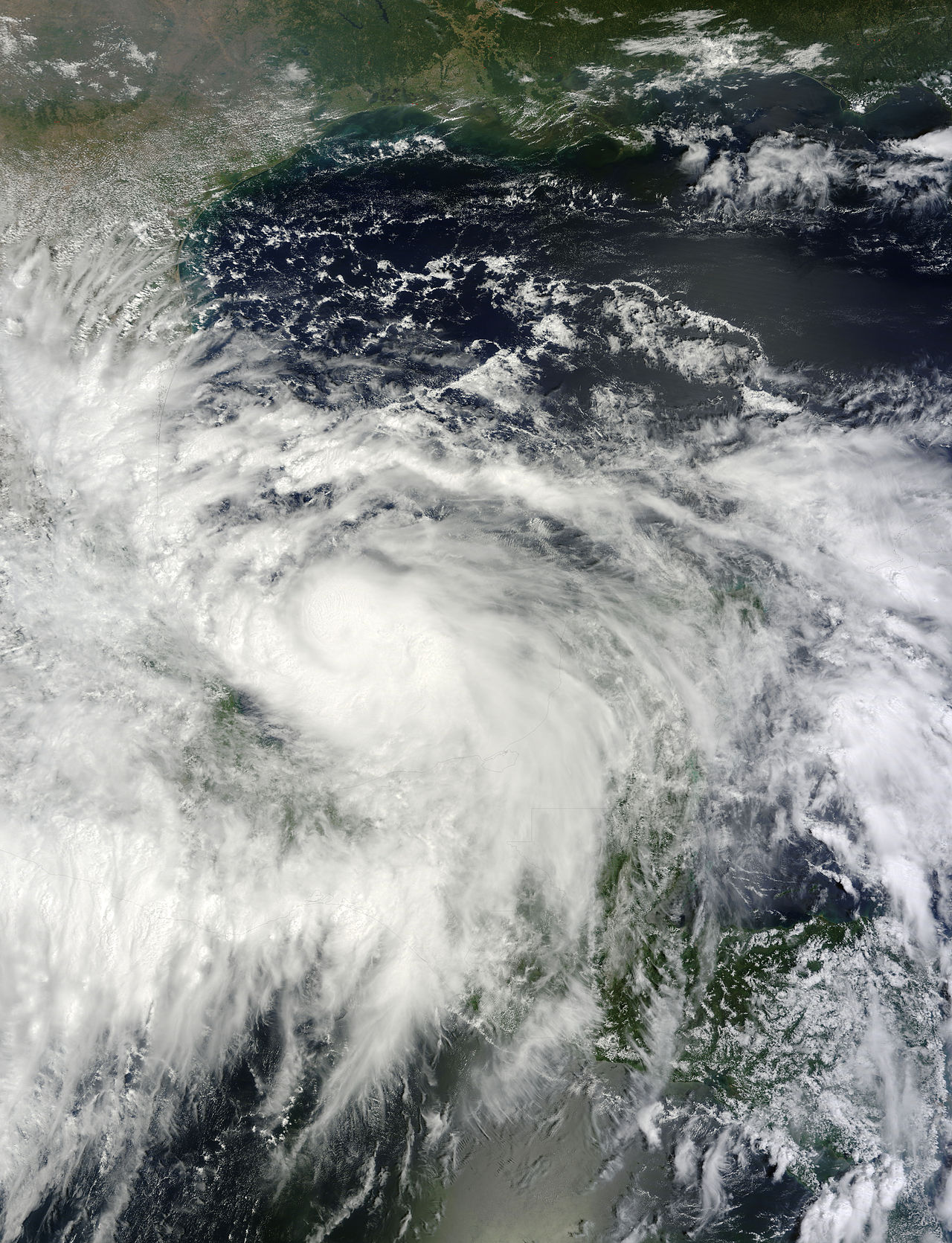
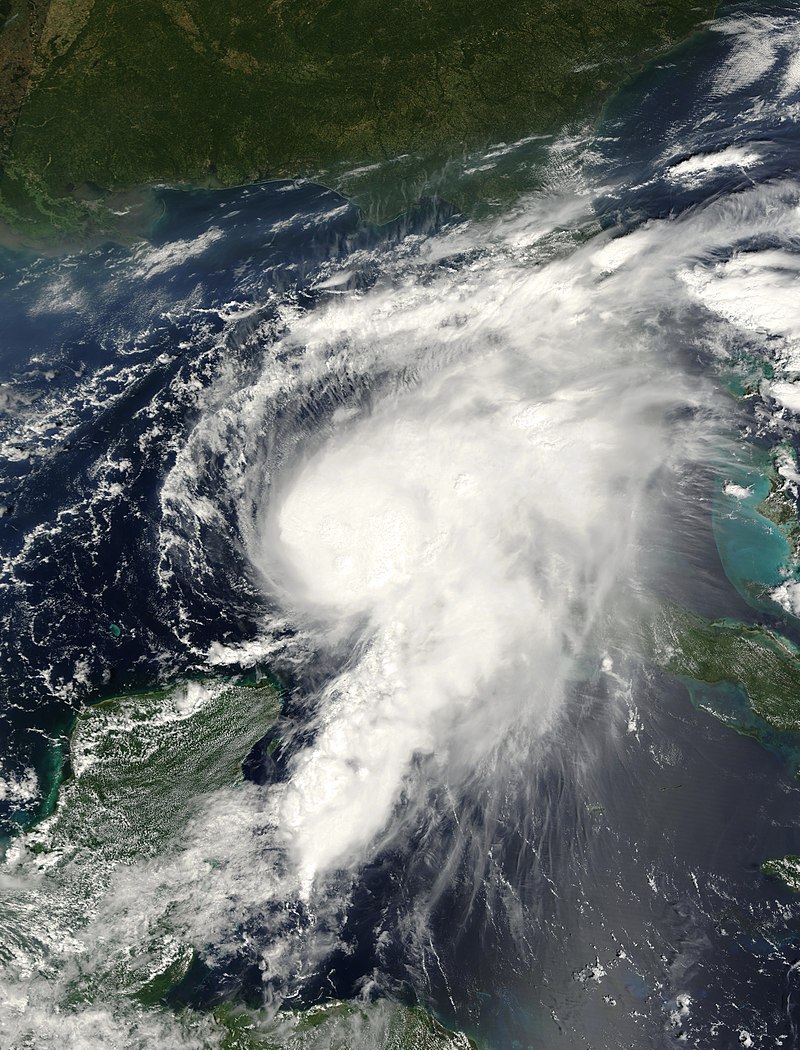
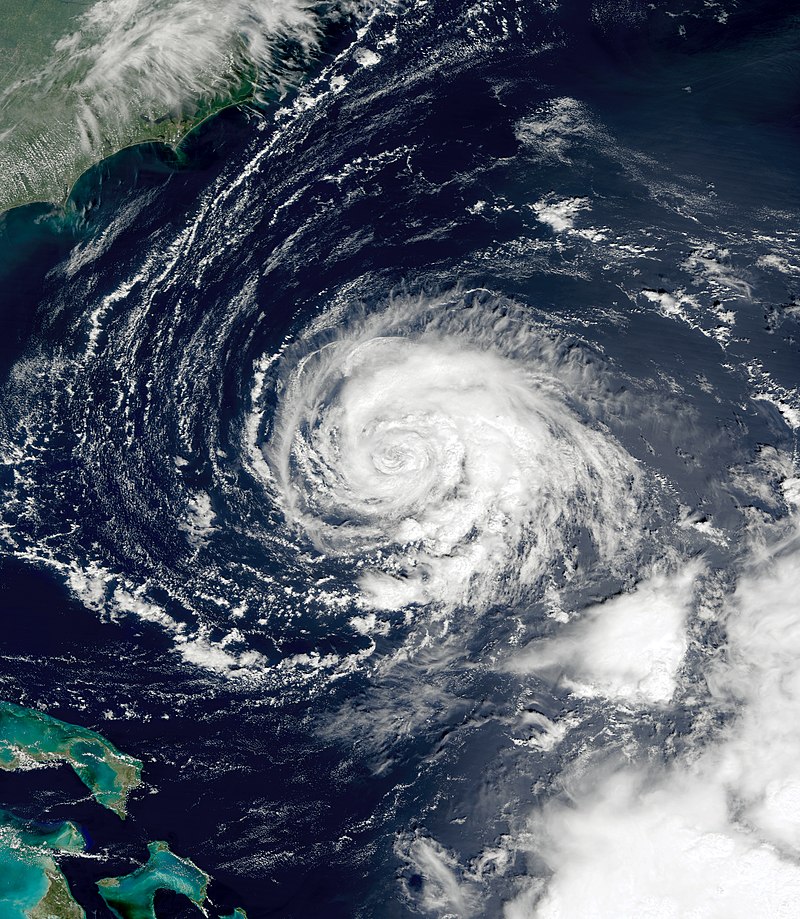
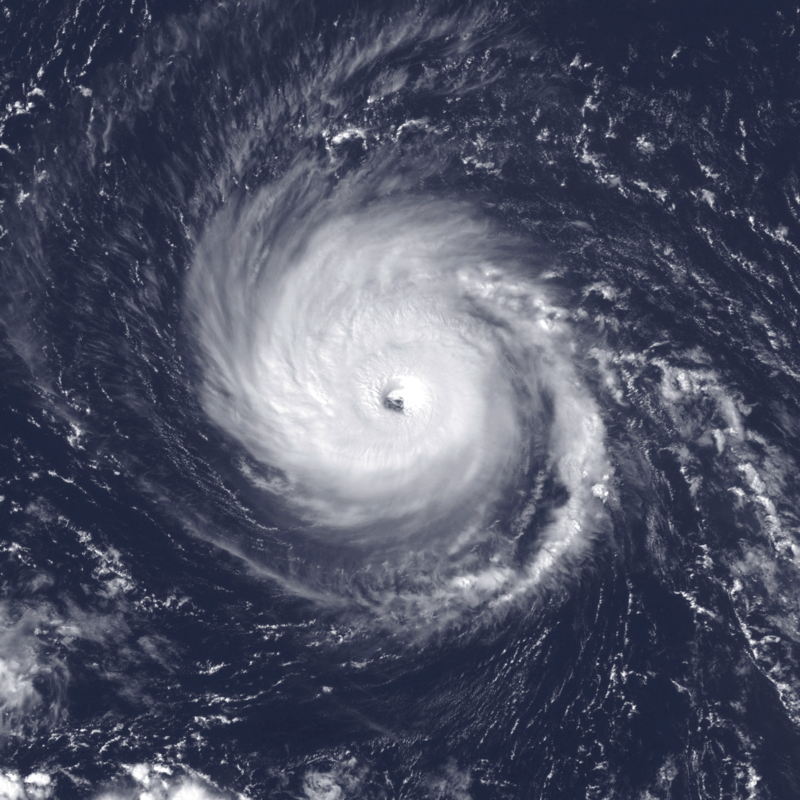
Formation and Track: On September 12, 2013, a tropical wave triggered the development of an area of low pressure in the Bay of Campeche, subsequently maturing into a tropical depression east-southeast of Veracruz. Initially, the slow movement of the depression was attributed to weak steering currents. By midday on September 13, the system strengthened into Tropical Storm Ingrid. After an initial westward trajectory towards Veracruz, the storm changed course and moved northeastward. Favorable conditions allowed for further intensification, and Ingrid reached hurricane status on September 14. With peak winds of 85 mph (137 km/h), the storm encountered increased wind shear, which gradually diminished its strength. Caught between weather systems, Ingrid took a sharp northwestward turn, eventually making landfall south of La Pesca, Tamaulipas, as a strong tropical storm on September 16. By September 17, the system had weakened into a tropical depression before dissipating.
Impact and Damage: Hurricane Ingrid, coupled with the simultaneous landfall of Hurricane Manuel, caused extensive damage and loss of life throughout the affected regions. The combined impact of the two storms affected approximately two-thirds of Mexico. In total, the storms claimed the lives of 192 individuals and resulted in billions of pesos in damages. Although the majority of the destruction was attributed to Hurricane Manuel, Hurricane Ingrid alone accounted for at least 23 fatalities and caused losses amounting to $20 billion pesos (MXN, US$1.5 billion).
The rainfall associated with Ingrid was particularly notable, with Tuxpan, Veracruz, experiencing peak precipitation of 20.1 inches (510 mm). Widespread flooding occurred, resulting in the damaging of over 14,000 houses, as well as significant impacts on infrastructure such as roads and bridges. Tamaulipas, the region where the storm made landfall, witnessed crop damage and river flooding. The effects of the storm also extended into southern Texas, causing high tides and localized flooding.
Enhancing Preparedness: In light of the devastating impact of Hurricane Ingrid, it is crucial to prioritize preparedness and resilience against future hurricane threats. To safeguard lives and minimize damage, residents in hurricane-prone areas should adhere to the following recommendations:
a) Stay informed: Monitor updates from reliable weather sources, such as the National Hurricane Center, to stay informed about approaching storms and their potential impacts.
b) Evacuation planning: Familiarize yourself with evacuation routes and shelters in your area. Develop a family emergency plan and ensure that essential supplies, including food, water, and medication, are readily available.
c) Secure property: Take necessary precautions to protect your home, such as reinforcing windows and doors, trimming trees, and securing loose outdoor objects. Install storm shutters or plywood to shield windows from high winds.
d) Flood protection: Purchase flood insurance, as standard homeowner’s insurance typically does not cover flood damage. Elevate essential appliances and utilities above the expected flood level, and consider installing barriers or flood-resistant materials in vulnerable areas.
e) Community preparedness: Engage with local authorities and participate in community emergency response initiatives. Encourage neighbors to prepare and collaborate in times of crisis.
Interesting Fact: As a direct result of Hurricane Ingrid and its unprecedented rainfall, the combined volume of rainwater produced by Ingrid and Hurricane Manuel was estimated to be around 5.7 trillion cubic feet (160 billion m3). This staggering amount is equivalent to the volume of every reservoir in Mexico combined. It serves as a testament to the immense power and water-carrying capacity of tropical cyclones and highlights the need for proactive measures to mitigate flooding and manage water resources in hurricane-affected regions.
In conclusion, Hurricane Ingrid in 2013 left a profound impact on Mexico’s eastern coastline, resulting in extensive damage, loss of life, and economic consequences. By understanding the storm’s formation, track, and impact, and by implementing effective preparedness measures, we can strive to enhance the resilience of communities in the face of future hurricane threats.



Leave a Reply