
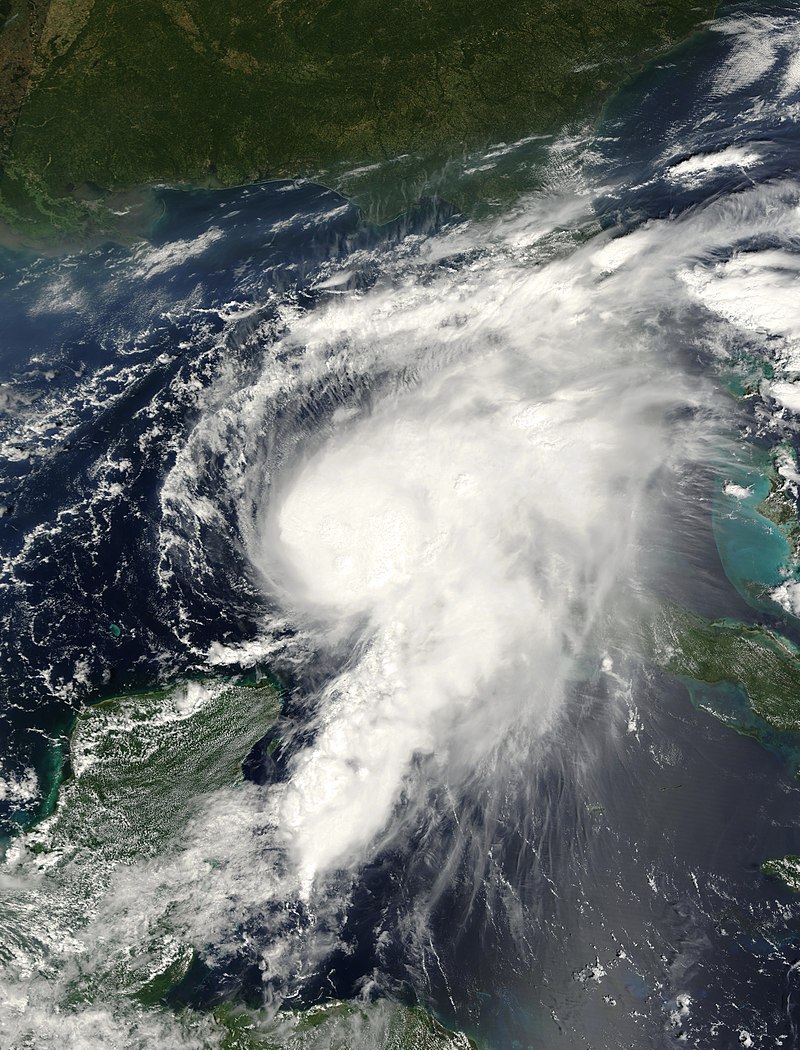
Hey there, friend! Have you ever wondered what it’s like to experience a hurricane firsthand? Hurricane Frederic landed on the Gulf Coast of the United States on September 12, 1979, leaving behind a trail of devastation and destruction. The storm caused havoc in various regions, including the Greater and Lesser Antilles, inland North America, and the Gulf Coast. With winds reaching 130 mph and causing damages worth $1.77 billion, Hurricane Frederic was considered one of the costliest storms on record. So buckle up and prepare for an insightful journey into how destructive Hurricane Frederic truly was during its reign in September 1979!
Overview of Hurricane Frederic

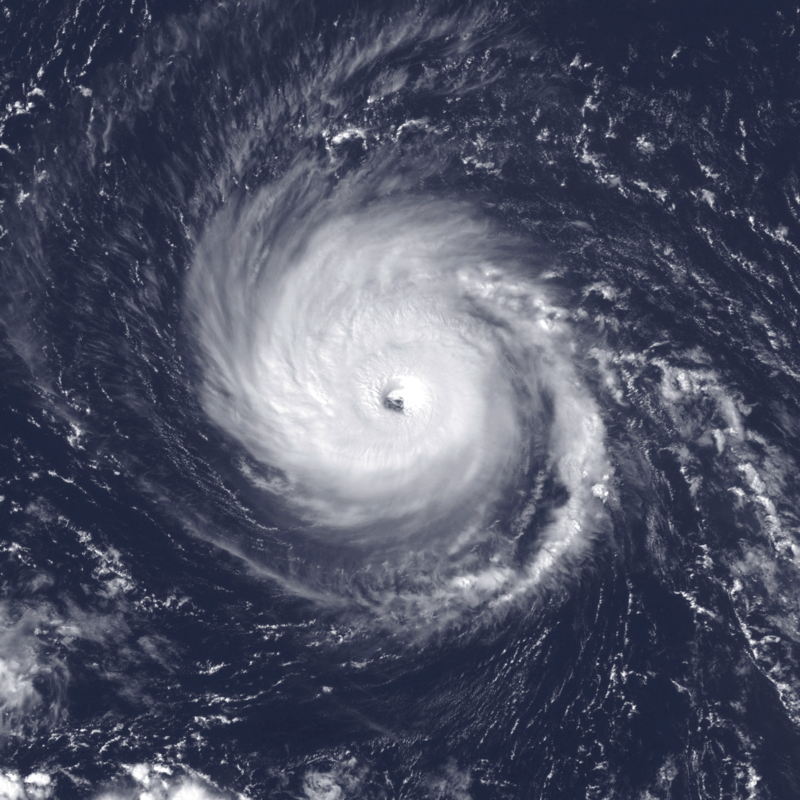
Hurricane Frederic was a tropical cyclone formed on August 29, 1979, in the Atlantic Ocean. The storm reached hurricane status on September 1, 1979. It caused extensive damage to various regions, including the United States Gulf Coast, Greater and Lesser Antilles, and inland North America. It landed as a Category 4 hurricane with sustained winds of around 130 mph near Dauphin Island, Alabama.
Frederic caused $1.77 billion in damage at the time of its occurrence – making it the costliest tropical cyclone on record until Hurricane Allen surpassed it two years later. The storm prompted several evacuation orders and watches/warnings in impacted regions – mostly impacting areas near Mobile Bay in Alabama.
FEMA was one of the key organizations in providing relief for those affected by Hurricane Frederic. Over $250 million in federal aid was provided for recovery efforts, with $188 million going towards Alabama alone. The aftermath of Hurricane Frederic demonstrated how destructive a storm can be even if it isn’t classified as a Category 5 hurricane and led to important lessons learned regarding disaster preparedness moving forward into future years.
Date and Location
Hurricane Frederic formed on August 29, 1979, from a tropical depression south of the Cape Verde Islands in the Atlantic Ocean. It reached hurricane status on September 1, 1979. However, outflows associated with Hurricane David weakened Frederic mid-way through its journey, causing it to weaken just before reaching Hispaniola.
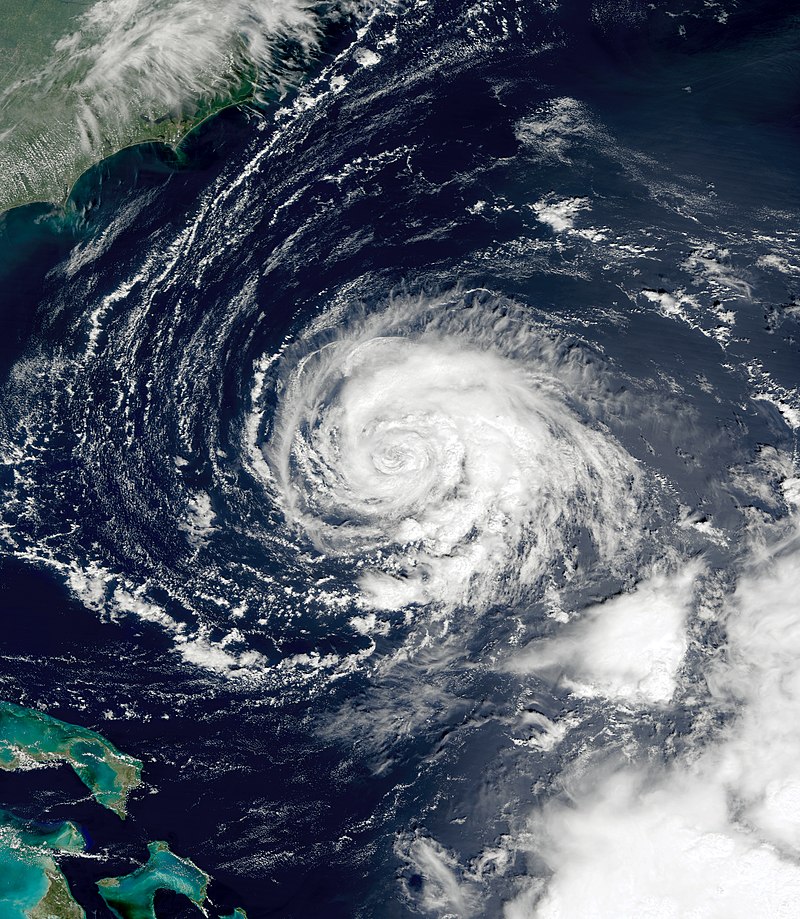
After nearly dissipating over Cuba, Hurricane Frederic redeveloped near the Isle of Youth and moved across the Gulf of Mexico, where it peaked with winds of around 130 mph on September 12th. The storm landed at Dauphin Island, Alabama as a Category 4 hurricane before weakening for a final time and becoming extratropical in Pennsylvania on September 14th.
Hurricane Frederic caused significant damage across various regions, including the United States Gulf Coast, Greater and Lesser Antilles, and inland North America. Despite being downgraded to Category Two by the time it hit Mobile County in Alabama’s Gulf coast region; it still caused significant destruction that changed landscapes permanently, like Pensacola Beach dunes restoration, which started right after Frederic ended.
As we explore further into this topic, we will take a closer look at some of these impacted regions and their respective damages in more detail.
Category and Intensity
Hurricane Frederic was a Category 4 hurricane that made landfall near Dauphin Island, Alabama, with sustained winds of 130 mph. At its peak intensity in the Gulf of Mexico, the storm ranks as one of the strongest hurricanes ever to hit the United States.
The storm’s Category 4 status meant it posed a significant threat to life and property along the Gulf Coast. The National Weather Service issued several watches and warnings leading up to Landfall Day. Evacuation orders were put in place for many communities in the area.
Although Hurricane Frederic was not as powerful as some other storms that have hit the United States, it still caused extensive damage and loss of life. In total, at least five people died due to this deadly storm.
The intensity of Hurricane Frederic is an important reminder that even smaller hurricanes can devastate coastal communities. As we continue to study tropical cyclones and their associated impacts, we must remain aware of how they can impact our lives and take steps to prepare for these events accordingly.
Impact of Hurricane Frederic
Hurricane Frederic caused extensive damage to various regions, including the United States Gulf Coast, Greater and Lesser Antilles, and inland North America. The storm made landfall at Dauphin Island, Alabama on September 12th, 1979 as a Category 4 hurricane with sustained winds of 130 mph. It caused almost $1.77 billion in damage, making it the costliest tropical cyclone on record at that time.
The storm was responsible for evacuating many people from the U.S. Gulf Coast – the largest ever up until that point. Many buildings were destroyed along the coast as strong winds flattened dunes and caused up to 15 feet of storm surge in some areas leading to five deaths across the impacted regions.
In the Pensacola area, Frederic hit, causing significant damage with heavy rainfall leading to large-scale flooding and dune erosion along the coast, destroying many structures. The Pecan industry took a hit from this storm as well, prompting many farmers to switch over to row crops after being utterly devastated by its effects.
Despite its Category 4 status upon reaching landfall in Alabama’s Gulf Beach region, where it set an all-time record low pressure at Mobile’s airport but still proved that you don’t have to be one of those higher category hurricanes like five or even four ones, such as Hurricane Andrew (1992) or Katrina (2005) just devastatingly catastrophic for anything – sometimes even just one natural disaster can cause absolute chaos!
Damage to Coastal Cities
Hurricane Frederic caused extensive damage to several coastal cities along the Gulf of Mexico. The storm hit Alabama’s Gulf Coast on September 12, 1979, as a category 4 hurricane with sustained winds of 130 mph. It caused around $2.3 billion in damages and led to five deaths in the county.
The storm flattened dunes and destroyed many structures along the coast. Some residents of Mobile went without power for weeks after the storm. The Pecan industry also took a significant hit from Hurricane Frederic, causing many farmers to switch to row crops instead.
In Florida, Pensacola Beach was among the areas heavily impacted by Hurricane Frederic’s strong winds and heavy rainfall. The storm destroyed many homes and significantly changed the landscape of the region’s beaches. Dune restoration efforts began immediately following the storm.
Overall, Hurricane Frederic proved that even a category 4 hurricane could cause catastrophic damage to communities along its path. Its effects were felt across several regions, including Puerto Rico and parts of inland North America. In fact, at $1.77 billion in damages in September 1979, it was considered one of the costliest tropical cyclones on record until then.\
Power Outages and Infrastructure Damage
Hurricane Frederic caused widespread power outages across the impacted regions, leaving millions without electricity for days and even weeks. In Alabama alone, roughly 700,000 people were left in the dark after the storm made landfall. The storm’s strong winds of up to 130 mph knocked down power lines and damaged transmission towers, making it difficult for utility crews to restore power quickly.
Apart from power outages, Hurricane Frederic also caused significant damage to infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings. One of the worst-hit areas was Pensacola Beach in Florida, where many homes were destroyed or severely damaged by the storm surge and high winds. Additionally, miles of dunes along the coast were flattened or washed away by the powerful waves.
The Bellingrath Gardens near Mobile suffered heavy damage due to fallen trees and limbs associated with Hurricane Frederic’s high winds. Moreover, several international gardens at Sarasota reported substantial losses from wind damage resulting from Hurricane Frederic’s aftermath.
The disruption caused by Hurricane Frederic’s sustained rainfall led to temporary water shortages across several areas, including Mississippi County in Arkansas and Pickens County in Alabama; additionally, the extremely heavy rainfall inundated farms across northern Georgia, causing extensive crop losses.
In conclusion, Hurricane Frederic caused widespread destruction not only through its strong Category 4 intensity but also through its impact on infrastructure such as roads and buildings as well as utilities like electrical grids that failed due to its effects on them. The aftermath of this hurricane shows how much work needs to be done in order for communities affected by these natural disasters can quickly recover when faced with similar scenarios again – we must learn our lessons so that history does not repeat itself!
Environmental Impact
Hurricane Frederic significantly impacted the environment in the areas it affected. The storm caused extensive damage to trees, gardens, and parks. According to reports from Bellingrath Gardens in Mobile County, Alabama, nearly 800 camellias were destroyed or damaged by the storm’s strong winds.
The storm surge also substantially affected the coastal ecosystems in areas like Dauphin Island and Pensacola Beach. The surge caused heavy damage along the coast, flattening dunes and destroying many structures. Dune restoration efforts began immediately after Frederic, but it would take months for these areas to recover fully.
In addition to physical damage, Hurricane Frederic also had lasting effects on local wildlife populations. The heavy storm led to flooding in some areas and disrupted habitats for various animal species. While specific numbers are unavailable for hurricane-related wildlife fatalities or injuries during Hurricane Frederic’s aftermath, hurricanes can significantly impact animal populations and their ecosystems.
Overall, Hurricane Frederic left a measurable environmental impact across several states and islands affected by this powerful tropical cyclone. Recovery efforts took years as communities worked tirelessly to restore their environments back to pre-storm conditions.
Government and Community Response

In the aftermath of Hurricane Frederic, government and community response was instrumental in helping those affected by the storm. Evacuation plans and procedures were put into place before the hurricane making landfall, and emergency services and relief efforts were quickly mobilized as soon as it was safe to do so.
One major aspect of government response was FEMA’s involvement in providing nearly $250 million in federal aid for recovery efforts. Most of this funding went to Alabama, which suffered the most damage from Hurricane Frederic. This aid helped provide necessary resources for rebuilding damaged infrastructure, homes, and businesses.
Additionally, many individuals within impacted communities came together to support each other during this difficult time. Volunteers assisted with removing debris, sheltering displaced individuals, and distributing food and water. Churches also played a significant role in offering their facilities as shelters and coordinating volunteer efforts.
Overall, it is clear that both government agencies and local communities worked together effectively to respond to Hurricane Frederic’s impact. While challenges were certainly faced by those affected by the storm, the collaborative effort demonstrated resilience in the face of disaster.
Keywords: hurricane Frederic,government, response,evacuation plans,FEMA,federal aid, recovery efforts,volunteers, damage,collaborative effort
Evacuation Plans and Procedures
Ahead of Hurricane Frederic, several evacuation plans and procedures were issued to ensure the safety of people in impacted areas. The storm prompted several evacuation orders and watches/warnings across different regions, including Florida, Mississippi, Alabama, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
In particular, the impacted areas around Mobile Bay were focused on evacuating many people from the Gulf Coast – reportedly the largest ever at that time. Furthermore, some 80 percent of residents in vulnerable coastal counties moved inland or to higher ground before Hurricane Frederic hit land.
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) was responsible for issuing guidance for potential impact areas during this Atlantic hurricane season, including Hurricane Frederic. It would take hours for officials to analyze weather data from various sources before finally issuing an alert about any possible hurricane formation; however, it wasn’t until September 1st that they classified it as a tropical depression south-east of Cape Verde Islands.
This proactive approach helped many communities prepare ahead of time by shutting down businesses temporarily while also activating their emergency response plans.
Despite being a Category 4 hurricane with sustained winds reaching up to 130mph and storm surges measuring up to 15ft tall in some Gulf Beaches, efforts made before landfall minimized loss of human life and property damage significantly.
Emergency Services and Relief Efforts
Something went wrong
Lessons Learned from Hurricane Frederic
Hurricane Frederic provided valuable lessons for future storm preparations and response efforts. One of the key takeaways was the importance of evacuation plans and procedures. The storm prompted one of the largest evacuations in U.S. history at the time, with over 500,000 Gulf Coast residents forced to flee their homes. This experience highlighted the need for established evacuation routes, adequate shelters, and communication systems between emergency management officials and local communities.
Additionally, Hurricane Frederic underscored the importance of infrastructure preparedness for power outages and damage caused by strong winds and heavy rainfall. Since then, many coastal cities have implemented measures such as underground utility lines, stronger building codes, and reinforcement of critical facilities like hospitals and police stations against hurricane winds through structural engineering programs that use high-quality materials including stainless steel pipe supports from manufacturers like Globe Composite Solutions.
Frederic also demonstrated that accurate weather forecasting is key to successful preparation efforts when a deadly tropical cyclone looms on the horizon. While early forecasts indicated that Florida would be heavily impacted by Frederic’s path through the Gulf of Mexico, further updates adjusted this forecast northward towards Mobile Bay instead.
Finally, Hurricane Frederic served as an example of how storms with lower intensity categories can still cause devastating damage to communities across affected areas during landfall events involving sharp turns into shoreline regions or inland penetration patterns near highly-populated areas with low-lying elevation features close by water bodies such as bays or rivers.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Hurricane Frederic

The impact of Hurricane Frederic was felt for years after the storm had passed. The devastation caused by this natural disaster changed the landscape of many coastal regions and highlighted the need for better emergency management procedures. Many areas affected by the storm have since recovered, but it is evident that some scars remain.
Despite being downgraded to a Category 2 hurricane at landfall, Hurricane Frederic caused excessive damage due to its sustained winds and heavy rainfall. It is estimated that the total damage cost $1.77 billion, making it one of the costliest tropical cyclones on record at the time.
In terms of legacy, Hurricane Frederic has left an enduring impact on those directly affected by it. Lessons learned from this event have helped shape emergency response efforts in future disasters and improved our understanding of how storms can cause such catastrophic damage.
Overall, while we cannot change what happened during Hurricane Frederic’s arrival or its aftermath, we can ensure we are prepared for any potential future storms and work towards minimizing their impact as much as possible through careful planning and coordination between government agencies and local communities.
Factual Data:
– Hurricane Frederic occurred in September 1979 during the Atlantic hurricane season
Frederic caused extensive damage to various regions, including the United States Gulf Coast, Greater and Lesser Antilles, and inland North America
Frederic caused $1.77 billion in damage, making it the costliest tropical cyclone on record at the time
The storm was responsible for evacuating a massive number of people from the U.S. Gulf Coast, the largest ever at the time
The storm prompted several evacuation orders and watches/warnings in the impacted regions
Frederic formed on August 29, 1979, from a tropical depression south of the Cape Verde Islands
The storm reached hurricane status on September 1, 1979, but outflow from Hurricane David weakened it mid-way through its journey
Frederic nearly dissipated over Cuba before redeveloping near the Isle of Youth
Frederic peaked in the Gulf of Mexico with winds of 130 mph on September 12, 1979, shortly before making landfall at Dauphin Island, Alabama
Frederic weakened for a final time before becoming extratropical in Pennsylvania on September 14 and dissipating the next day
Frederic caused $5 million in damage both in Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, with an additional $1.7 billion in damage on the mainland United States
FEMA was the focal point for nearly $250 million in federal aid for recovery, with $188 million going to Alabama
Frederic hit the Alabama Gulf Coast on September 12, 1979, as a Category 4 hurricane with 130 mph winds
The storm caused damage along the Gulf Coast, costing around $2.3 billion and leading to five deaths
The storm caused up to 15 feet of storm surge in some Gulf Beaches
Many buildings were destroyed along the coast, and some residents of Mobile went without power for weeks
The Pecan industry took a hit from the storm, and many farmers switched to row crops
Hurricane Frederic set an all-time record low pressure at Mobile’s airport
Hurricane Frederic occurred in September 1979 and directly struck Mobile with an impact far beyond, causing devastation to communities
The storm proved that you don’t have to be a Category 5 storm to cause catastrophic damage
Hurricane Frederic hit the Pensacola area in September 1979, causing a lot of damage and changing the landscape of the region’s beaches, including Pensacola Beach
The storm caused heavy damage along the coast, destroying many structures and flattening dunes
Dune restoration began right after Frederic and cont



Leave a Reply